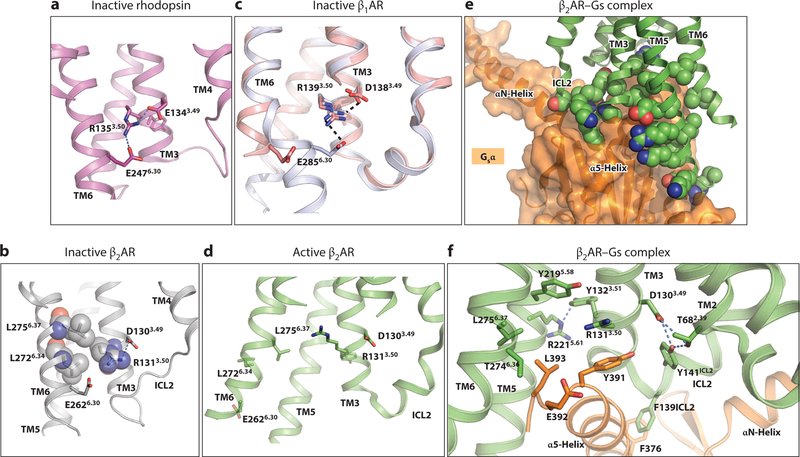
Figure 3.
The conserved D(E)RY motif in the G protein–binding site. (a) The ionic lock in dark rhodopsin formed by R1353.50 and E2476.30. (b) The ionic lock is not present in the crystal structure of carazolol-bound β2AR. The packing of R3.50 with L2726.34 and L2756.37 is shown with space-filling models of these side chains. (c) Two conformations of the ionic lock region are observed in inverse-agonist bound structures of the β1AR. Bending near the cytoplasmic end of TM6 results in an electrostatic interaction between R1393.50 and E2856.30 ( gray; PDB 2YCX). The alternative straight conformation of TM6 (salmon; PDB 2VT4) moves these two residues apart. (d) Movements of TM6 and TM7 in the β2AR active state prevent ionic lock formation, and the intrahelical salt bridge between D1303.49 and R1313.50 is broken. (e) Packing of β2AR ( green, with side chains in space-filling representation) and Gsα (orange, shown as a transparent surface). ( f) Interactions of β2AR with the C-terminal region of bound Gsα. Gsα is shown in orange. Polar interactions are shown with dashed lines. Abbreviations: β2AR, β2-adrenergic receptor; G sα, Gsβ, stimulatory heterotrimeric G protein α and β subunits; PDB, Protein Data Bank; TM, transmembrane.