FIG 2.
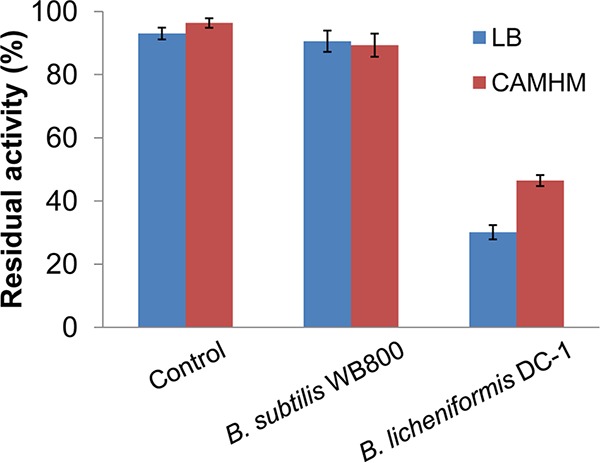
Colistin is degraded by the fermentation supernatant of Bacillus species bacteria. The residual antibacterial activity of colistin was determined by the cylinder-plate diffusion method in both LB agar and CAMHM. E. coli DH5α was used as the test strain. An amount of 200 μl of LB or CAMH broth (control) or fermentation supernatant of Bacillus bacteria was pipetted into stainless steel cylinder cups. The plates were left standing for 12 h at 4°C and then incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The diameters (in mm) of inhibition zones were accurately measured by vernier caliper. The residual antibacterial activity of colistin was calculated according to the following formula: residual activity (%) = (residual concentration/initial concentration) × 100. Each reaction was performed in triplicate. Error bars show standard errors of the means (SEM).
