FIG 3.
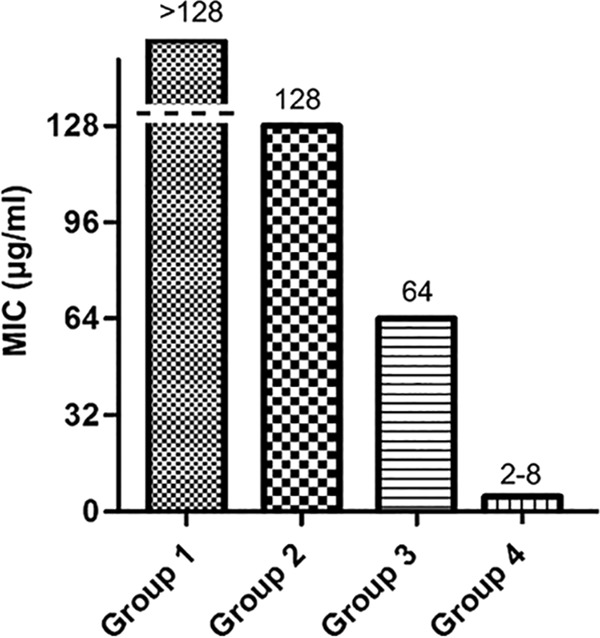
ZnLla has no antibacterial activities against non-Helicobacter strains. The MICs were determined by broth microdilution assays as described in Materials and Methods. The strains used were divided into four groups based on MIC values. The MIC for group 1 is >128 μg/ml, and the strains include Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Pseudomonas putida PAO1, Enterococcus faecalis FA2-2, Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028, Moraxella catarrhalis ATCC 25238, Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606, Mycobacterium smegmatis MC2 155, Bacillus subtilis 168, Enterococcus faecium ATCC 19434, Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619, Proteus mirabilis ATCC 29906, Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49766, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans D7S-1, and Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. The MIC for group 2 is 128 μg/ml, and the strains include Enterobacter cloacae ATCC 13047, Campylobacter jejuni NCTC11168, Escherichia coli MG1655, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 35657, Lactococcus lactis MG1363, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia ATCC 51331, and Morganella morganii ATCC 25830. The MIC for group 3 is 64 μg/ml, and the strains include Neisseria gonorrhoeae ATCC 19424 and Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. The MIC for group 4 is 2 to 8 μg/ml, and the strains include 20 H. pylori strains.
