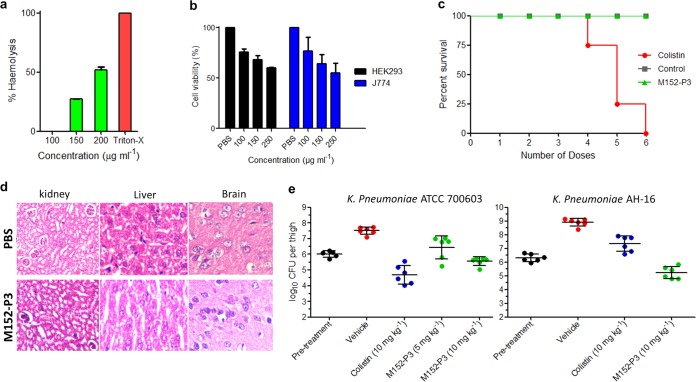
FIG 4.
Low in vitro and in vivo toxicity of M152-P3 and efficacy in thigh infection models of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae. (a) Hemolysis assay with rabbit RBCs. No lysis of RBCs at up to 100 μg ml−1 was observed. The data are plotted as mean ± SD of three replicates. (b) In vitro mammalian toxicity in HEK 293 and J774 cell lines. The data shown here are mean ± SD of three replicates. (c) Acute toxicity study in mice (n = 4). Six doses (12 mg/kg) of M152-P3 or colistin were given subcutaneously at 2-h intervals. No mouse in the colistin group could tolerate the six doses, whereas the M152-P3 group showed no deaths at the administered dose and the mice behaved similarly to the placebo group. (d) Histopathology of major organs of mice after the six-dose administration. M152-P3 showed no significant changes in any of the organs, and results were comparable to those observed with PBS. (e) In vivo efficacy of M152-P3 in the thigh infection model (six mice in each group). K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 was injected intramuscularly in the right thigh, and single-dose treatment was given subcutaneously after 4 h. Values of CFU per thigh were determined 24 h postinfection. The vehicle group received PBS. In the case of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae AH-16, treatment was given 2 h and 11 h postinfection, and the mice were sacrificed 24 h postinfection. CFU for each mouse were calculated in duplicate, and the average values are plotted. Each point in the graph represents one mouse. The data are plotted as mean ± SD.