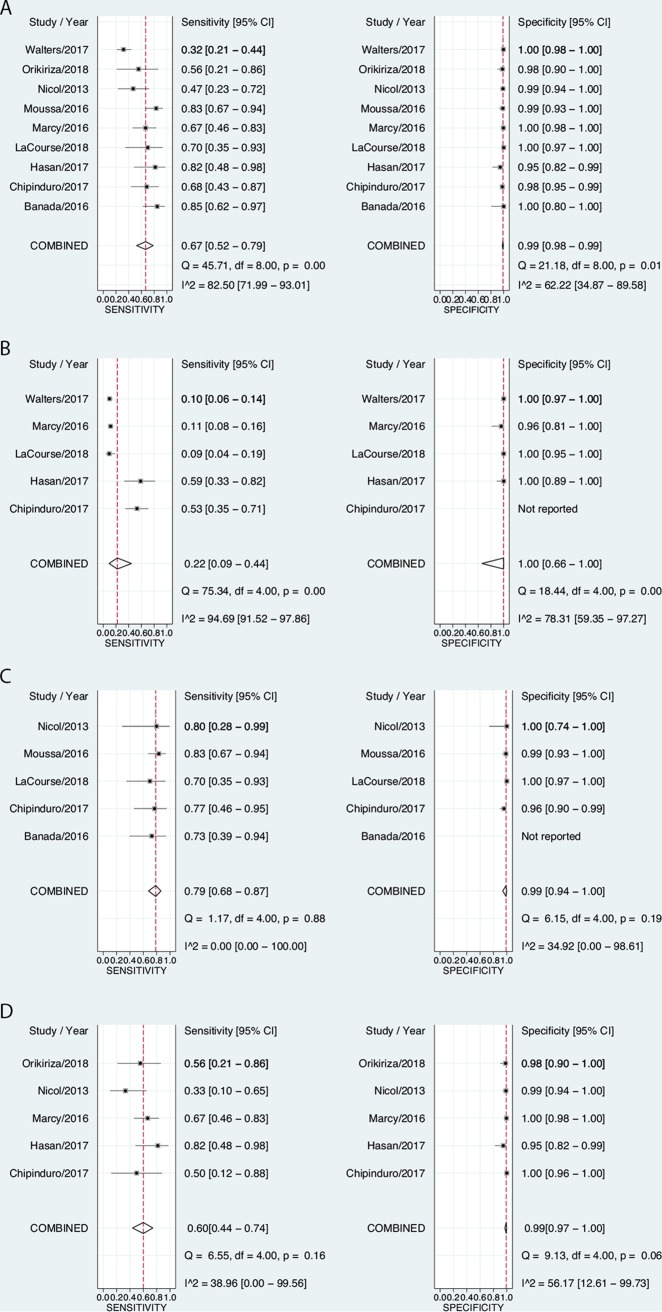
FIG 3.
(A) Forest plots of stool Xpert’s diagnostic performance compared to a microbiological reference standard of culture or Xpert positivity on respiratory samples (14–22). Two studies (18, 20) presented results from “intention-to-treat” (ITT) analyses, where any child who produced any sample was included, as well as “per-protocol” analyses, where only children who produced all requested samples were included. In these instances, we meta-analyzed the ITT results to avoid selection bias. (B) Forest plots of stool Xpert’s diagnostic performance compared to a clinical reference standard of “likely/possible TB” or “unlikely TB.” (C) Forest plots of diagnostic performance of stool Xpert in children with HIV compared to a microbiological reference standard. (D) Forest plots of diagnostic performance of stool Xpert in HIV-negative children compared to a microbiological reference standard.