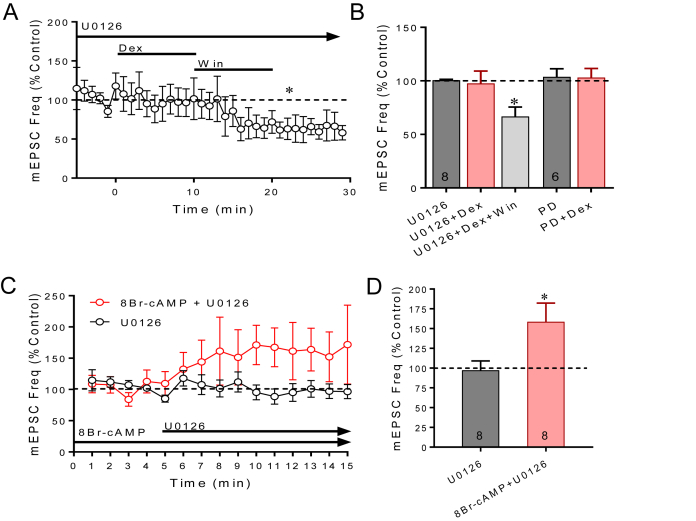
Fig. 3.
ERK-MAP kinase activation is required for glucocorticoid-induced suppression of excitation. A. Running average of mEPSC frequency in the presence in the bath perfusion of the MEK inhibitor U0126 (25 μM). U0126 blocked the effect of Dex (1 μM) on the frequency of mEPSCs but did not block the decrease in the mEPSC frequency caused by activation of presynaptic CB1 receptors with Win55,212-2 (Win, 5 μM), suggesting ERK/MAPK dependence of glucocorticoid signaling. B. Summary bar graph of the effect of the MEK inhibitors U0126 and PD 0325901 on the Dex-induced suppression of mEPSCs. The MEK inhibitors blocked the suppression of mEPSC frequency by Dex but not by the CB1 agonist WIN55,212-2. C. The PKA-induced endocannabinoid suppression of mEPSCs is dependent on ERK-MAPK activity. The MEK inhibitor U0126 applied alone had no effect on mEPSC frequency but caused an increase in mEPSC frequency following the intracellular application of the PKA activator 8Br-cAMP via the patch pipette. D. Summary bar graph of mean effects of blocking ERK-MAPK activity with U0126 in the absence and presence of the PKA activator 8-Br-cAMP in the patch pipette (cAMP + U0126). *, p < 0.05.