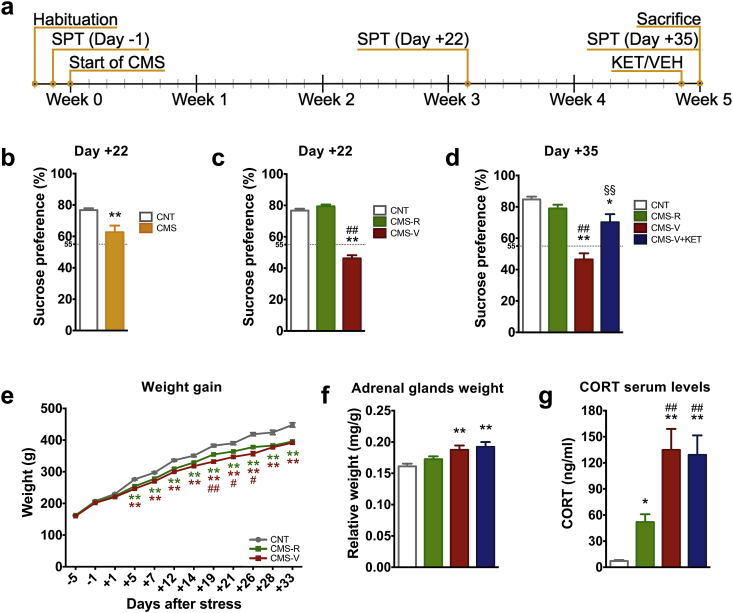
Fig. 1.
(a) Experimental plan: animals were subjected to a variable sequence of mild stressors for five weeks. Sucrose preference test (SPT) was performed to evaluate anhedonic behavior. KET or vehicle (VEH) were acutely administered 24 h before sacrifice. (b) SPT of CNT and CMS rats at Day +22 of CMS. n = CNT 101; CMS 188. Unpaired t-test: **p < 0.001 vs CNT; (c) Separation of resilient and vulnerable animals applying a cut-off at 55% of sucrose preference at Day +22 of CMS. n = CNT 101; CMS-R 100; CMS-V 88. (d) SPT of CNT and CMS rats at Day +35 of CMS, 24 h after KET/VEH treatment n = CNT 59; CMS-R 53; CMS-V 27; CMS-V + KET 25. (e) Body weight gain; n = CNT 101; CMS-R 100; CMS-V 88. (f) Adrenal glands weight. n = CNT 54; CMS-R 48; CMS-V 25; CMS-V + KET 21. (g) CORT serum levels. n = CNT 30; CMS-R 27; CMS-V 15; CMS-V + KET 15. Data are shown as means ± standard error of the mean. TPHT: *p < 0.05 vs CNT; **p < 0.001 vs CNT; #p < 0.05 vs CMS-R; ##p < 0.001 vs CMS-R; §§p < 0.001 vs CMS-V.