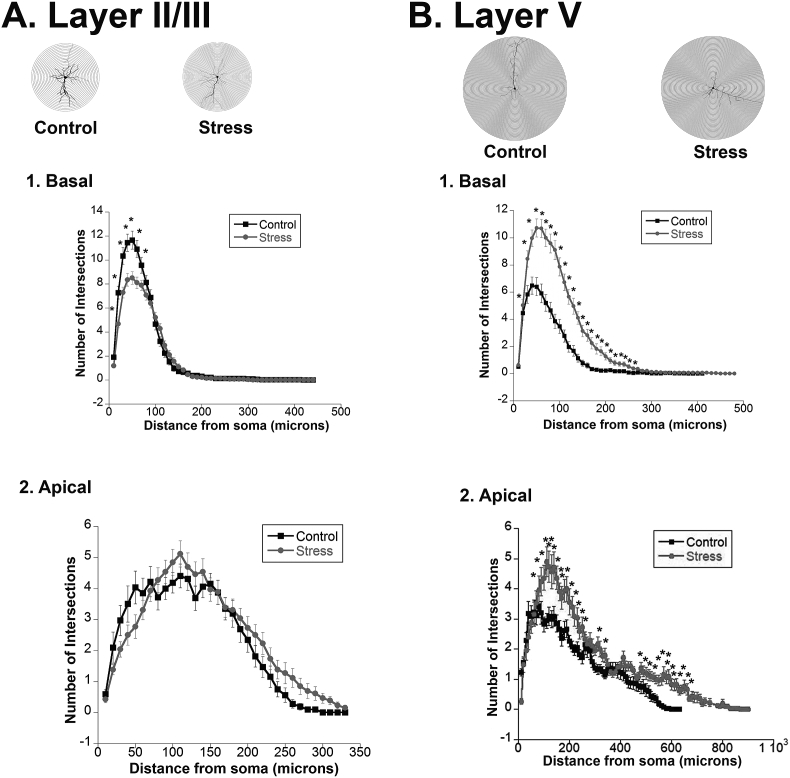
Fig. 2.
Dendritic Arborization and Complexity in Adult Males. Sholl analysis was run on adult male neurons in layer II/III and layer V, using 20 μm concentric rings. Intersections of dendrites with each concentric ring were recorded. Group size = 34 cells/4 rats for controls, 30 cells/4 rats for defeats. A. Layer II/III.1. Basal Dendrites. Repeated social stress decreased the complexity as measured by number of intersections. 2. Apical Dendrites. There was no effect of stress. B. Layer V.1. Basal Dendrites. Repeated social stress increased the complexity as measured by number of intersections. 2. Apical Dendrites. Repeated social stress increased the complexity as measured by number of intersections.