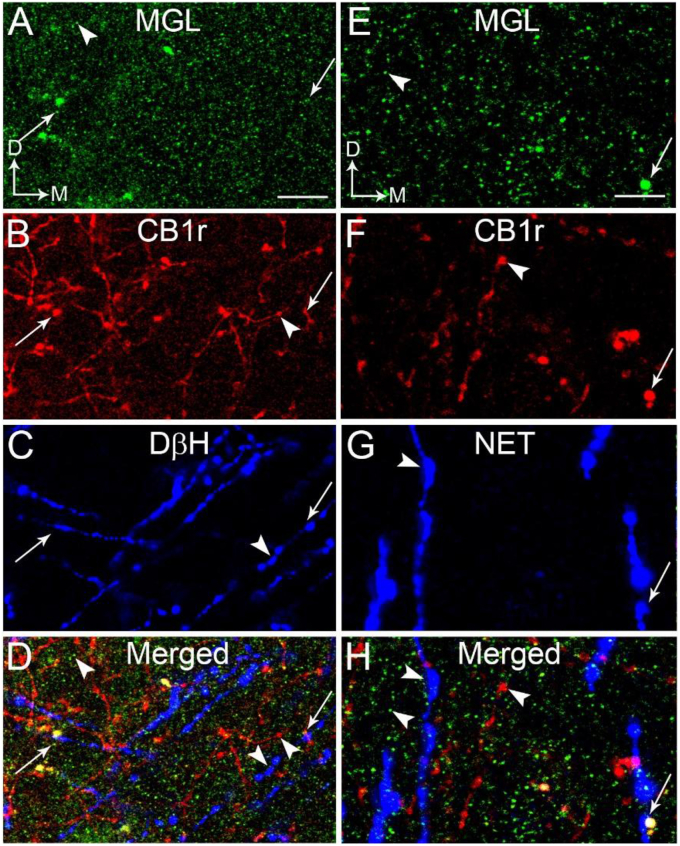
Fig. 5.
A-D. Confocal fluorescence photomicrographs showing immunolabeling of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1r) and dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DβH) in the frontal cortex. MGL was detected using a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) donkey anti-rabbit IgG (green); CB1r was detected using a tetramethylrhodamine-5-isothiocyanate (TRITC)-conjugated donkey anti-guinea pig IgG (red) and DβH was detected using a Cy5-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG (blue). CB1 and DβH appeared as punctate processes. The merged image (panel D) shows colocalization of MGL, CB1r and DβH in the same process (arrows). Arrowheads indicate single-labeled MGL, CB1r or DβH. Thick arrows indicate dual labeling (MGL and DβH or CB1r and DβH). E-H. Confocal fluorescence photomicrographs showing immunolabeling of MGL, CB1r and norepinephrine transporter (NET) in the frontal cortex. MGL was detected using a FITC donkey anti-rabbit IgG (green); CB1r was detected using a TRITC-conjugated donkey anti-guinea pig IgG (red) and NET was detected using a Cy5-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG (blue). CB1r and NET appeared as punctate processes. The merged image (panel H) shows colocalization of CB1 and NET in the same process (arrows) that is in close proximity with a MGL-labeled profile. Arrowheads indicate single-labeled MGL, CB1r or NET. Thick arrows indicate dual labeling (MGL and DβH or CB1 and DβH). Scale bars: 30 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)