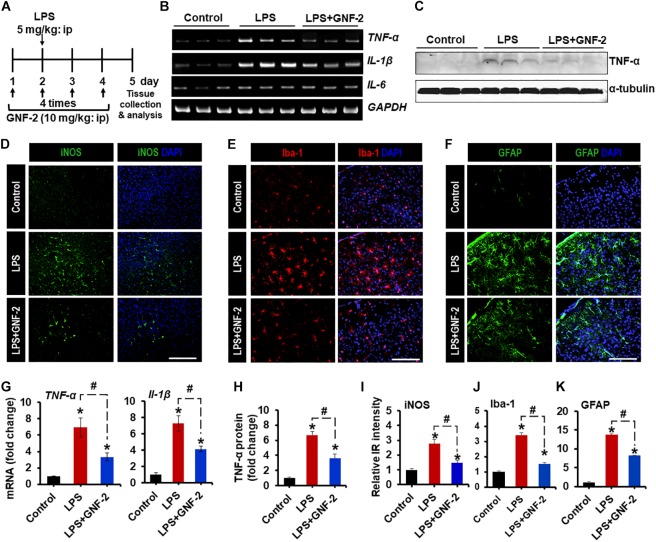
FIGURE 5.
Effects of GNF-2 administration on LPS-induced neuroinflammation in vivo. (A) To determine the role of c-Abl in neuroinflammation, GNF-2, and LPS were administered intraperitoneally at the indicated time points as shown in the experimental outline. (B) The expression of TNF-α and IL-1β mRNAs in the brain tissues after GNF-2 and LPS injection was evaluated by conventional RT-PCR. (C) The western blot detection of TNF-α protein in the brain tissue after GNF-2 and LPS injection. (D–F) The immunoreactivity (IR) of iNOS, Iba-1, and GFAP was increased in the brain of LPS-injected mice, whereas GNF-2 administration significantly attenuated this increase in IR. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. (G) Quantification for the TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA expression is displayed as the fold change of gene expression normalized to GAPDH. (H) Quantification for the TNF-α protein from the western blot. (I–K) Quantification for the relative intensities of iNOS, Iba-1, and GFAP IR is presented in the graph. ∗p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated control animals; #p < 0.05 between the indicated groups; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test; n = 3 for each group; data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bar 400 μm (D), 200 μm (E,F).