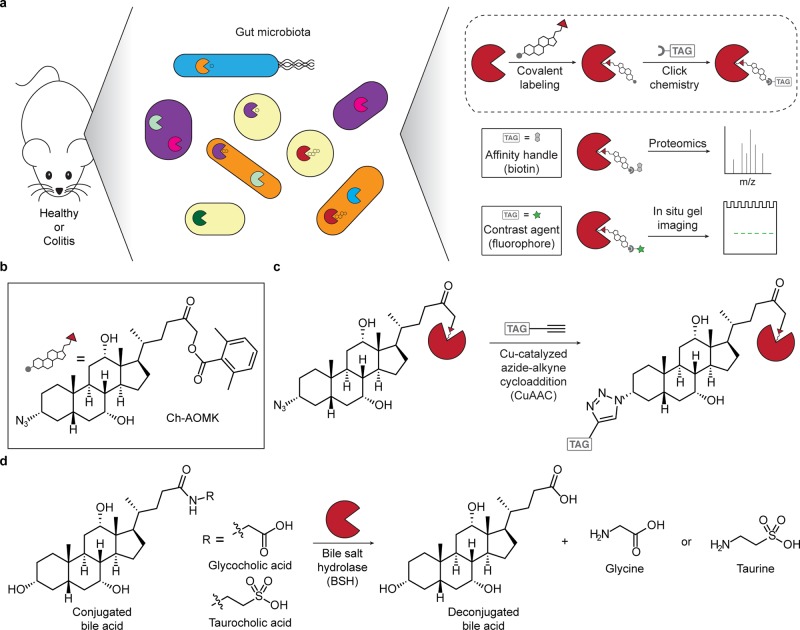
Figure 1.
Chemoproteomic, activity-based approach for profiling bile salt hydrolase (BSH) activity within the gut microbiome during health and disease (e.g., colitis). (a) Scheme of overall chemical strategy to covalently label active BSH enzymes via their active-site cysteine. (b) Structure of the activity-based probe Ch-AOMK used to identify BSH activity in the gut microbiome. (c) Cu-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) click chemistry reaction to tag labeled enzymes with an affinity handle or contrast agent (e.g., TAG) for pull-down or imaging of BSH activity. (d) BSH carries out the deconjugation reaction of glyco- and tauro-conjugated bile acids, which is the first major step of bile acid metabolism in the intestines.