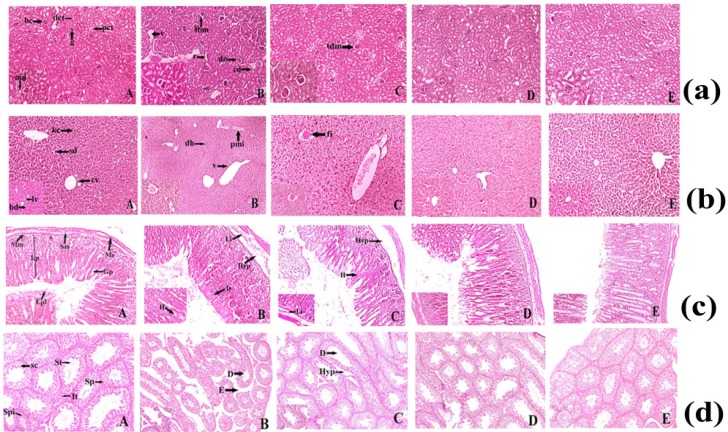
Figure 4.
(a) Histopathological representation of Kidney of Sprague Dawley Rat. (A) Normal histopathological appearance of kidney tissue showing Bowman's capsule (bc), Macula densa (md), Proximal convoluted tubule (pct), Distal convoluted tubule (dct) of control Swiss Albino Mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (B) Histological appearance of kidney tissue of ruthenium-baicalein complex (400 mg/kg) treated rat showing thickening of capsular membrane (tbm), ruptures (r), desquamated nuclei (dn), vacuolization (v), (H&E) 10X and 40 X. (C)Thickening of capsular membrane was observed at 200 mg/kg dose level of ruthenium-baicalein complex, (H&E) 10X and 40X. (D)Histological appearance of kidney of ruthenium-baicalein complex (100 mg/kg) Swiss Albino Mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (E) Histological appearance of kidney of ruthenium-baicalein complex (50 mg/kg) Swiss Albino Mice(H&E) 10X and 40X. (b) Histopathological representation of Swiss Albino Mice's liver. (A) Normal histological architecture of liver of control group showing the Central vein (cv), Bile duct (bd), Sinusoidal dilation (sd), Kupffer cell (kc), Lymph vessel (lv) of control Swiss Albino Mice(H&E) 10X and 40X. (B) & (C) Histological appearance of liver of ruthenium-baicalein complex (400 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg) treated rats showing periportal mononuclear infiltrates (pmi), degeneration of hepatocytes (dh), focal inflammation (fi) (H&E) 10X and 40X. (D) Histological appearance of liver of ruthenium-baicalein complex (100 mg/kg) treated mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (E) Histological appearance of liver of ruthenium-baicalein complex (50 mg/kg) treated mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (c) Representative histopathological picture of Swiss Albino Mice stomach. (A) Normal pathological architecture of stomach of control group showing Muscularis externa (me), Submucosa (sm), Muscularis mucosa (mm), Lamina propia (lp), Gastric pit (gp), epithelial lining (epl) of control Swiss Albino Mice (H&E) 10X and 40X.(B) & (C) Histological appearance of stomach of ruthenium-baicalein complex (400 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg) treated mice showing Hemorrhages (h) between villus, Hyperplasia (hyp), leukocyte infiltration (Li) (H&E) 10X and 40X. (D) Histological appearance of stomach of ruthenium-baicalein complex (100 mg/kg) treated mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (E) Histological appearance of stomach of ruthenium-baicalein complex (50 mg/kg) treated mice (H&E) 10X and 40X. (d) Representative histopathological picture of Swiss albino Mice testis. (A) Normal physiological architecture of testis of control Swiss albino Mice showing Sertoli cell (sc),Spermatogonia (Sp), Seminiferous tubule (St), Interstitial tissues (It) is seen within the tubular lumen. (H&E) 4X and 10X.(B) Histopathological appearance of testis of ruthenium-baicalein complex (400 mg/kg) treated rat showing Edema in interstitial tissue (E), Degeneration of seminiferous tubule (D). (H&E) 4X and 10X.(C) Histopathological appearance of testis of ruthenium-baicalein complex (200 mg/kg) treated mice showing the degeneration of seminiferous tubules (D) and hyperplasia (Hyp). (H&E) 4X and 10X.(D) Histological appearance of testis of ruthenium-baicalein complex (100 mg/kg) Swiss albino Mice (H&E) 4X and 10X.(E) Histological appearance of testis of ruthenium-baicalein complex (50 mg/kg) Swiss albino Mice (H&E) 4X and 10X.