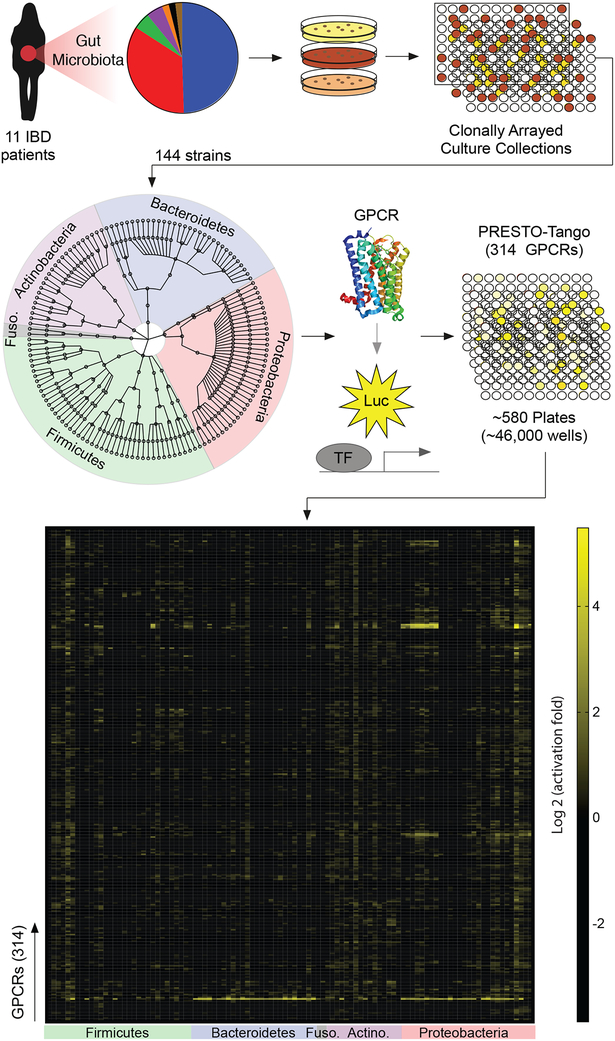
Figure 1. A forward chemical genetic screen identifies human gut microbes that activate GPCRs.
We isolated 144 unique human gut bacteria spanning five phyla, nine classes, eleven orders, and twenty families from 11 inflammatory bowel disease patients via high-throughput anaerobic culturomics and massively barcoded 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Bacterial isolates were grown in monoculture in a medium specialized for the cultivation of human gut microbes (gut microbiota medium) and supernatants from individual bacterial monocultures were screened against the near-complete non-olfactory GPCRome (314 conventional GPCRs) using Parallel Receptor-ome Expression and Screening via Transcriptional Output-Tango (PRESTO-Tango).