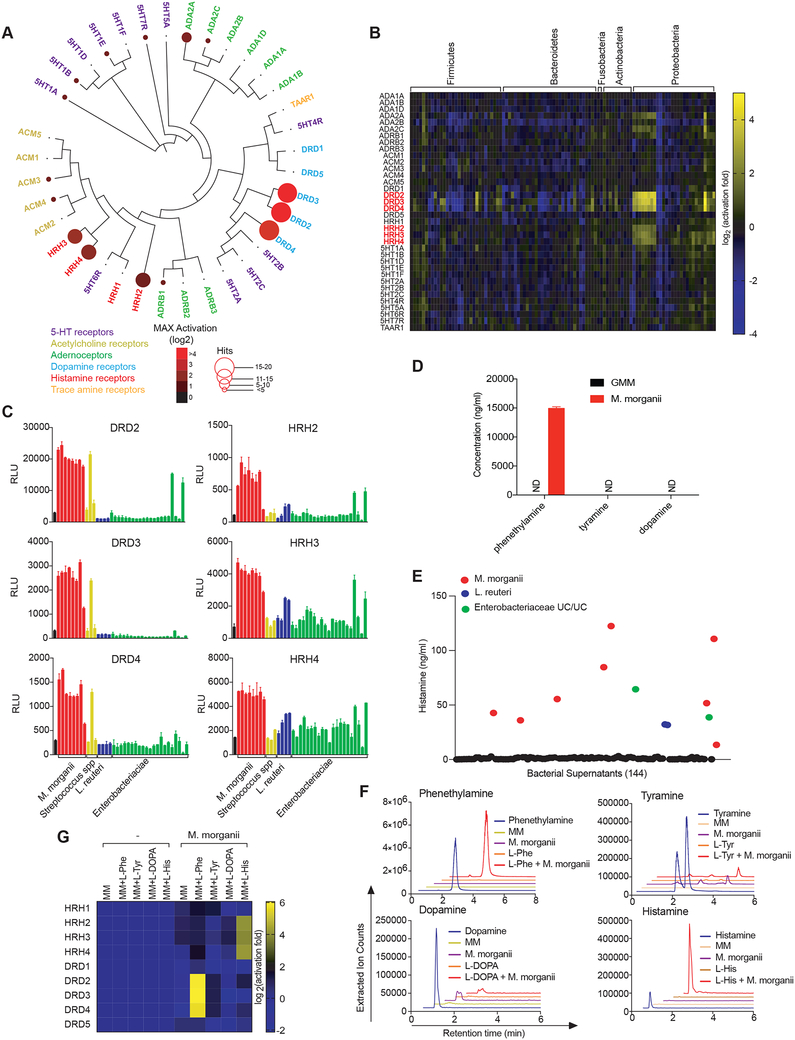
Figure 3. Diverse human gut bacteria activate aminergic GPCRs.
(A) Activation of aminergic GPCRs by metabolomes from a human gut microbiota culture (see Figure 1). GPCR activation was measured by PRESTO-Tango. Screening results are displayed on a phylogenetic tree of aminergic GPCRs. Color intensity represents magnitude of activation over media alone and radii of the circles represents the number of bacteria that activated a given GPCR by more than two-fold over media alone.
(B) Heatmap depicting the activation of aminergic GPCRs by metabolites from a human gut microbiota culture collection as measured by PRESTO-Tango. Fold induction over stimulation with bacterial media alone is depicted on a log2 scale.
(C) Activation of DRD2–4 and HRH2–4 by select species and strains as measured by Tango assays.
(D) Quantification of dopamine, phenethylamine and tyramine production by M. morganii. Supernatants from 24-hour cultures of M. morganii C135 in gut microbiota medium were analyzed by Triple Quadrupole-Mass Spectrometry (QQQ-MS/MS).
(E) Quantification of histamine production by 144 isolates of human gut bacteria by ELISA (48 hr. cultures).
(F) Mass spectrometric traces of metabolite production by M. morganii C135. M. morganii was cultured in minimal medium (MM) with or without additional L-Phe, L-His, L-Tyr or L-DOPA for 48 hours. Metabolite production was analyzed by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
(G) M. morganii-derived phenethylamine and histamine activate DRD2–4 and HRH2–4, respectively. M. morganii C135 were cultured as described in F and supernatants were screened for activity against DRDs and HRHs by PRESTO-Tango.
Data for all panels other than A and B are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n=3 replicates per group (C-G).