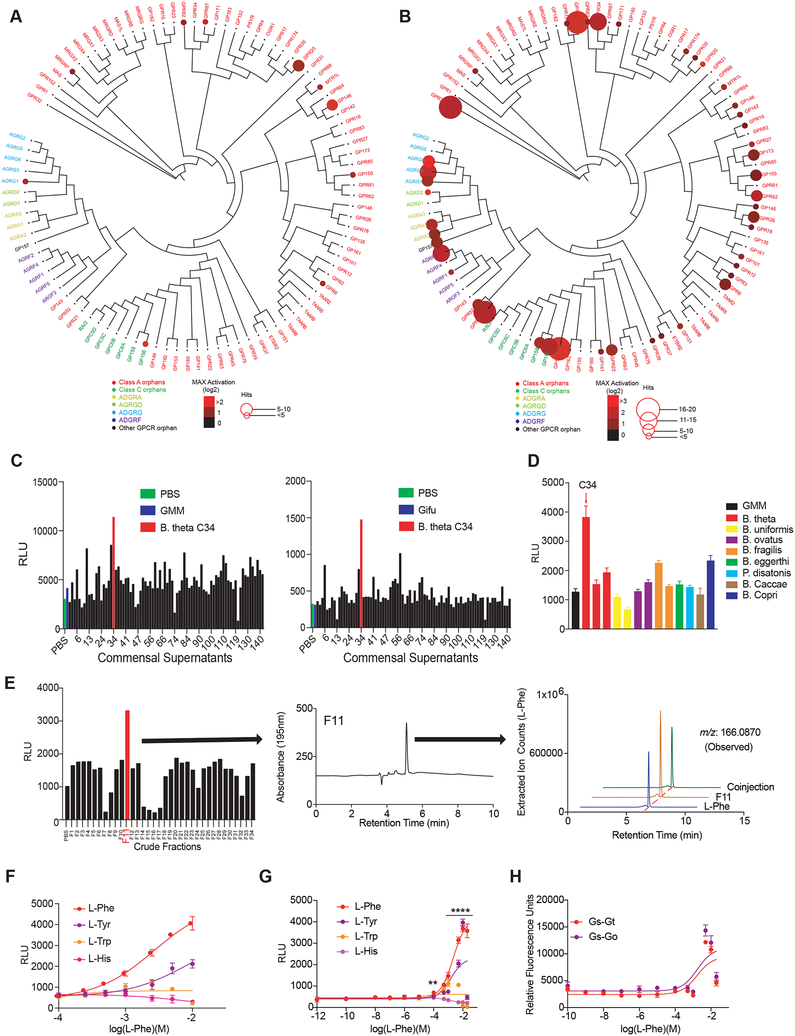
Figure 6. A unique strain of B. thetaiotaomicron C34 is a prolific producer of LPhe and activates GPR56/AGRG1.
(A and B) Activation of orphan GPCRs by metabolomes from a human gut microbiota culture (see Figure 1) grown in gut microbiota medium (A) or Gifu (B) as measured by PRESTO-Tango. Screening results are displayed on a phylogenetic tree of orphan GPCRs that was constructed and visualized with equal branch lengths using gpcrdb.org, PHYLIP and jsPhyloSVG. Color intensities represent the magnitude of activation over media and radii of circles represent the number of bacteria that activated a given GPCR by more than two-fold.
(C) A single isolate C34 assigned to the species Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron activates GPR56/AGRG1 when cultured in gut microbiota medium (GMM: top panel) or Gifu medium (bottom panel). Activation of GPR56/AGRG1 by supernatants from 144 human gut isolates was measured via GPR56-Tango.
(D) B. theta strain C34 uniquely activates GPR56/AGRG1. Activation of GPR56/AGRG1 by supernatants from diverse species and strains from the genera Bacteroides and Parabacteroides cultured in GMM was measured via GPR56 PRESTO-Tango.
(E) B. theta C34-produced L-Phe activates GPR56/AGRG1. B. theta C34 supernatants were fractionated via reversed-phase HPLC and fractions were evaluated for activation of GPR56/AGRG1 via GPR56-Tango. The active fraction (F11) contained a primary constituent that was identified via LC-MS, HRMS-ESI-QTOF, NMR, and advanced Marfey’s analyses as LPhe.
(F and G) L-Phe activates the orphan receptor GPR56/AGRG1. Activation of GPR56/AGRG1 by titrating doses of pure L-Phe, L-Tyr, L-Trp, and L-His was measured via GPR56-Tango using RPMI 1640 medium (F) or a custom medium lacking L-Phe and L-Tyr (G).
(H) L-Phe activates G protein-dependent signaling downstream of GPR56/AGRG1 as measured by the CRE-SEAP assay. Gαs-Gαt and Gαs-Gαo chimeras were used to redirect GPR56/AGRG1 signaling to Gαs.
Data in all panels except for A, B, and E are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.