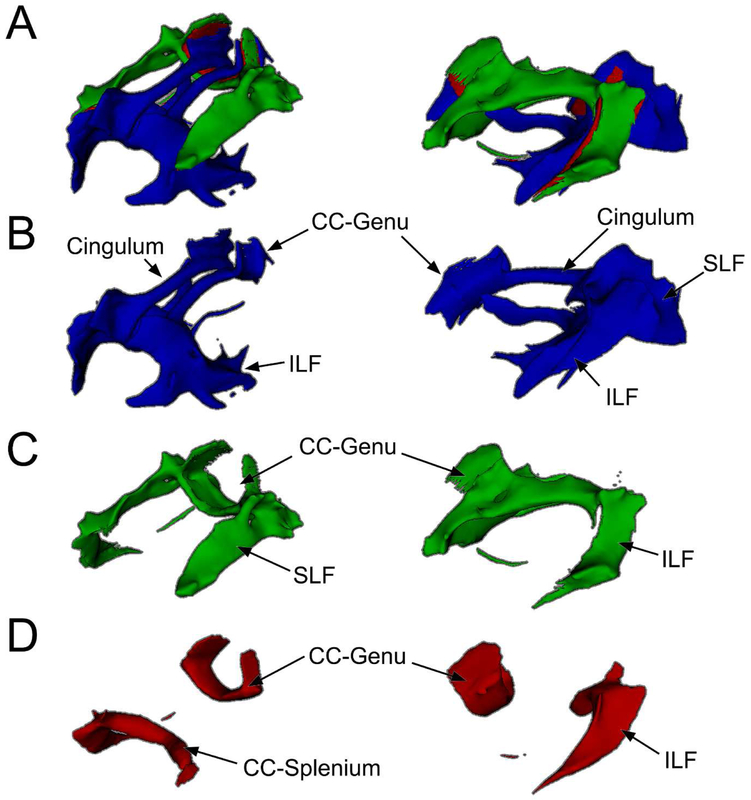
Figure 2. DMN and ECN WM Templates.
A: WM pathways connecting the DMN (blue) and ECN (green) with areas connecting both shown in red. B: WM pathways unique to the DMN include portions of the corpus callosum (CC) splenium and genu, cingulum, superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), and inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF). C: WM pathways unique to the ECN include portions of the SLF, CC-genu, and ILF. D: WM pathways that connected both DMN and ECN regions included portions of the CC genu and splenium and ILF. A-D: WM pathways were identified using probabilistic tractography and averaging individual results to form a single group template. The regions identified in the functional templates (Figure 1) were used as seeds for tractography. Superior-lateral view on left and lateral view on right.