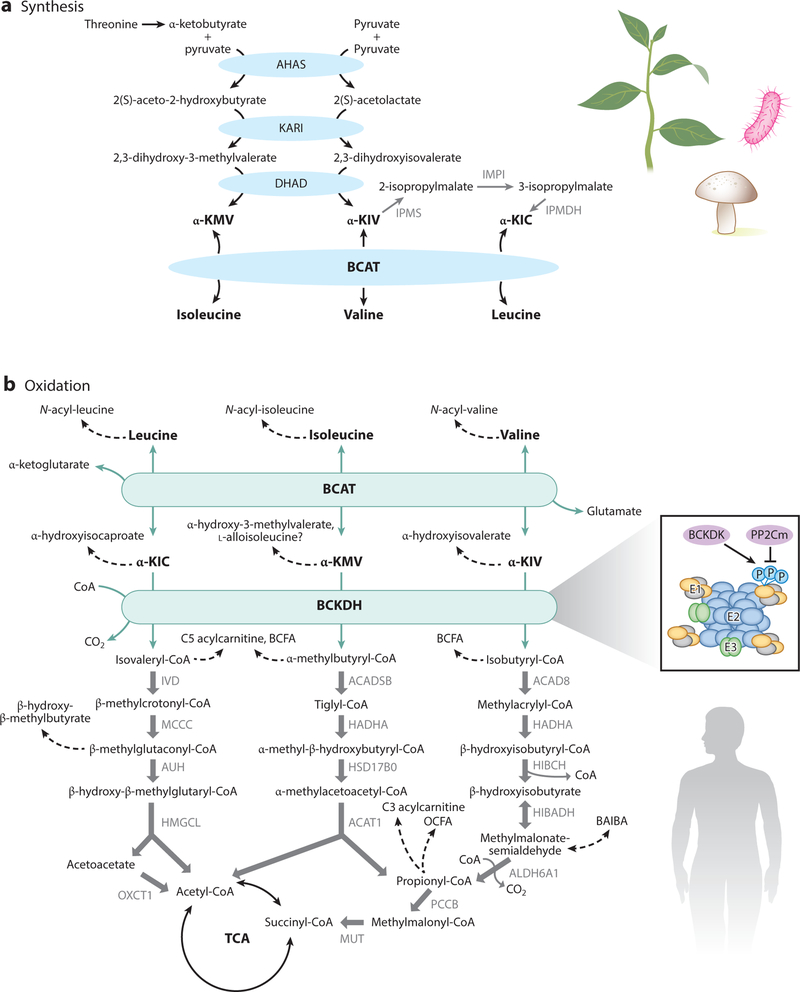
Figure 1.
BCAA synthesis and catabolism. Synthesis (a) occurs in plants, bacteria, and fungi. Oxidation (b) occurs in plants, bacteria, fungi, and animals. All three BCAAs share the BCAT and BCKDH steps, after which catabolism of each BCAA is unique. The BCKDH complex is composed of a core of 24 E2 subunits, which are docked by E1 heterotetamers and E3 dimers. BCKDK inhibits E1 via phosphorylation, which is reversed by PP2Cm. Abbreviations: ACAD8, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 8; ACADSB, short/branched chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ACAT1, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1; AHAS, acetohydroxyacid synthase; α-KIC, α-ketoisocaproic acid; α-KIV, α-ketoisovaleric acid; α-KMV, α-ketomethylvaleric acid; ALDH6A1, aldehyde dehydrogenase 6 family member A1; AUH, AU RNA-binding protein/enoyl-coenzyme A hydratase; BAIBA, beta-amino-isobutyric acid; BCAA, branched chain amino acid; BCAT, branched chain amino transferase; BCFA, branched chain fatty acid; BCKDH, branched chain amino acid dehydrogenase; BCKDK, BCKDH kinase; CoA, coenzyme A; DHAD, dihydroxyacid dehydratase; HADHA, hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase subunit alpha; HIBADH, 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase; HIBCH, 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase; HMGCL, 3-hydroxymethyl-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase; HSD17B0, 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase; IPMDH, isopropylmalate dehydrogenase; IPMI, isopropylmalate isomerase; IPMS, isopropylmalate synthase; IVD, isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase; MCCC, methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase; MUT, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase; OCFA, odd-chain fatty acid; OXCT1, 3-oxoacid CoA transferase; P, phosphorylation; PCCB, propionyl-CoA carboxylase subunit beta.