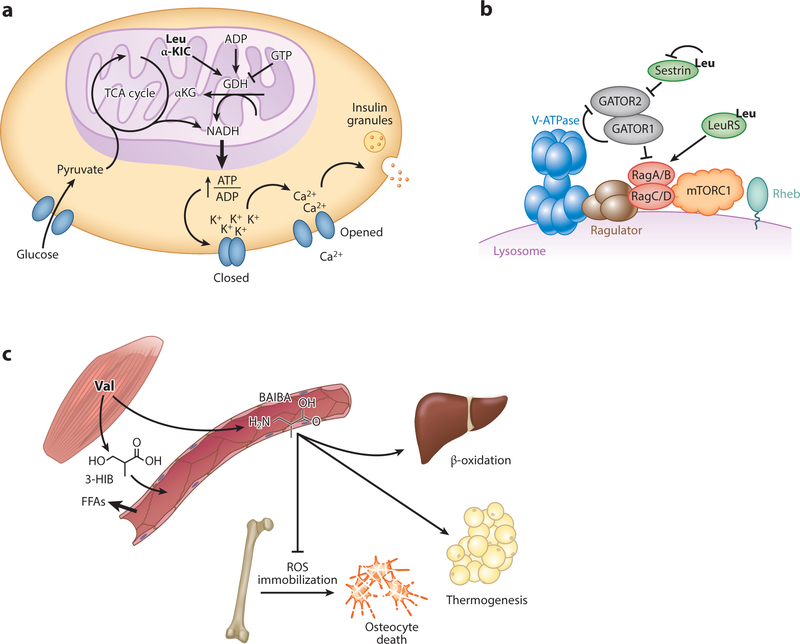
Figure 2.
(a) Leucine and α-KIC promote insulin release from pancreatic B cells via activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. (b) Leucine promotes mTORC1 activity by relieving Sestrin2-mediated inhibition and promoting LeuRS-mediated pathway activation. (c) Skeletal muscle secretes valine catabolites BAIBA and 3-HIB. BAIBA promotes hepatic B oxidation, adipocyte thermogenesis, and osteocyte survival; 3-HIB induces fatty acid transport across the endothelium and into skeletal muscle. Abbreviations: 3-HIB, 3-hydroxyisobutyrate; ADP, adenosine 5 -diphosphate; αKG, α-ketoglutarate; ATP, adenosine 5 -triphosphate; BAIBA, beta-amino-isobutyric acid; FFA, free fatty acid; GATOR1, GAP activity toward the Rag GTPases 1; GATOR2, GAP activity toward the Rag GTPases 2; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; Leu, leucine; LeuRS, leucyl tRNA synthetase; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Val, valine; v-ATPase, vacuolar H+-adenosine triphosphatase ATPase.