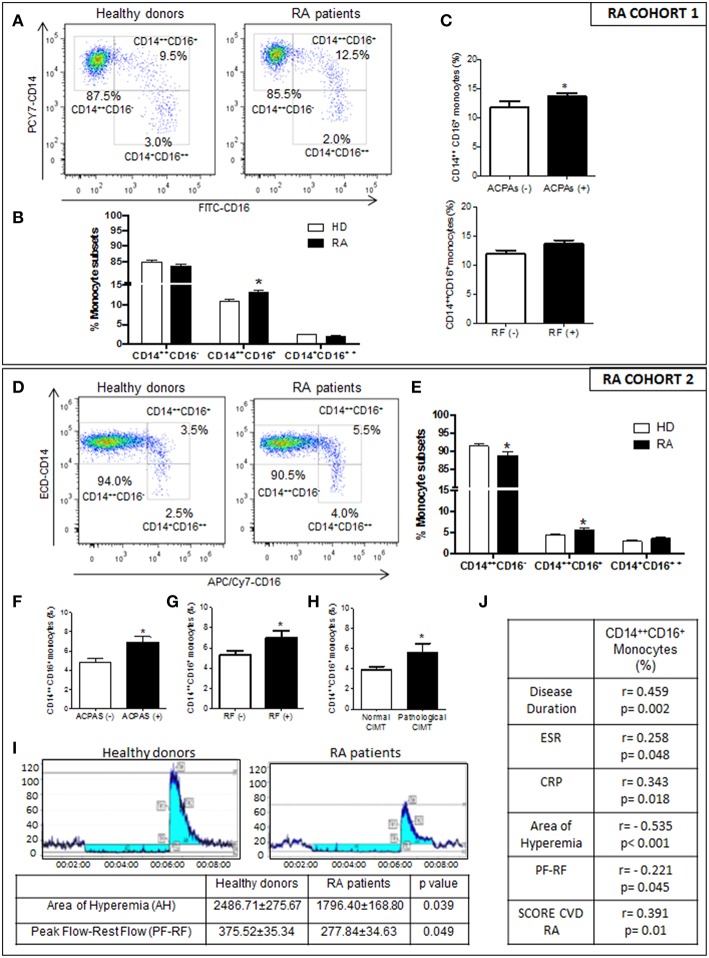
Figure 1.
Relationship of the increased intermediate monocyte subpopulation in RA patients with their immunologic and inflammatory profile, and association to endothelial dysfunction, CIMT and CV risk score. (A–C) PRECISESADS Cohort. (A) Representative dot plots of monocyte subtypes from RA patients and HDs. (B) Percentage of different monocyte subtypes by flow cytometry in whole blood of 140 RA patients and 145 HDs. (C) Association between increased frequency of intermediate monocytes and autoimmunity. (D–J) Second cohort: 50 RA patients and 33 HDs. (D) Representative dot plots of monocyte subtypes from RA patients and HDs. (E) Percentage of different monocyte subtypes by flow cytometry. (F–H) Association between increased frequency of intermediate monocytes with autoimmunity and pathological CIMT. (I) Impaired microvascular endothelial dysfunction in RA patients measured by Laser-Doppler. (J) Correlations between the percentage of intermediate monocytes and clinical parameters of the disease, endothelial dysfunction and SCORE CVD. Paired t-test was performed *indicates significant differences vs. HDs (p < 0.05).