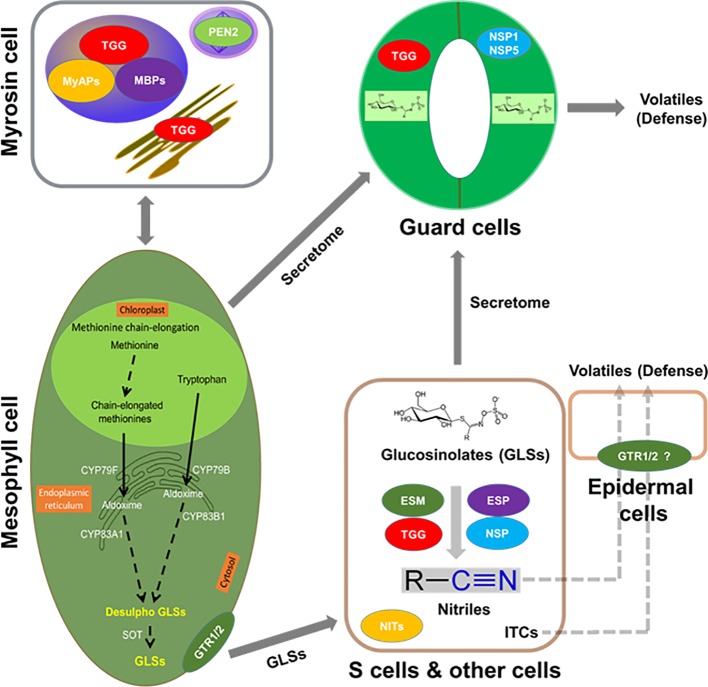
Figure 1.
Putative interactions between myrosinases (TGGs), myrosinase interacting proteins, GLSs, and volatiles in the context of cell type compartmentation. A myrosin cell shows vacuolar localization of TGGs, myrosinase-binding proteins (MBPs), and myrosinase-associated proteins (MyAPs); peroxisomal localization of penetration (PEN2); and ER localization of TGG. Transporters that are specific to GLSs such as NRT1/PTR glucosinolate transporter (GTR) 1, GTR2 or non-specific transporters could be aiding in their transport to site of accumulation such as S-cells or guard cells. Importantly, these cells may have the capability of de novo biosynthesis of GLSs. In addition, the presence of epithiospecifier modifier (ESM, MyAP-like), epithiospecifier (ESP), and nitrile specifier (NSP) 1, NSP5, etc. may lead to the breakdown of GLSs to nitriles and isothiocyanates (ITCs) for roles in cell type-specific signaling and defense against pathogen and herbivores. GLSs, TGGs, and ESP were found in the S-cells, and the presence of ESM and NSP is indicative of other cell types.