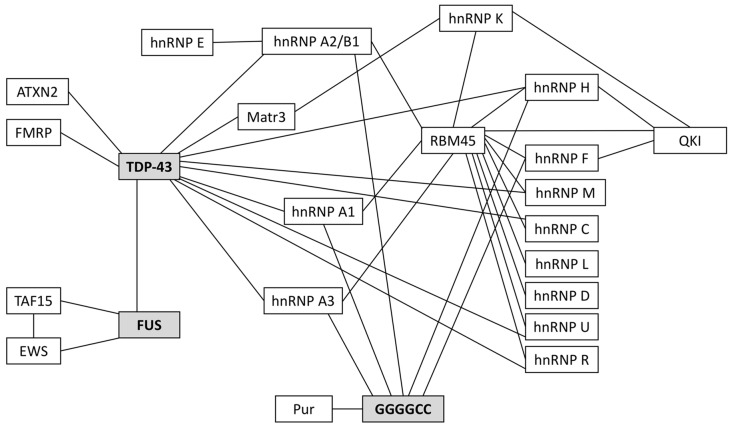
Figure 2.
Protein binding partners that have been implicated in ALS. 97–98% of ALS patients have pathogenic protein inclusions that stain positive for the RNA/DNA binding protein TDP-43. Most of the remaining 2%–3% of patients will have inclusions that stain positive for FUS. Currently, the most prevalent genetic mutation associated with familial and sporadic ALS is the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion (HRE); these patients characteristically have TDP-43-positive inclusions and/or TDP-43-negative, ubiquitin-positive inclusions and/or pathogenic RNA foci (composed of GGGGCC repeats), all of which are known to sequester RNAs and proteins. Many of the RNA-binding proteins in this schematic are critical for RNA trafficking and local translation of key mRNAs in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.