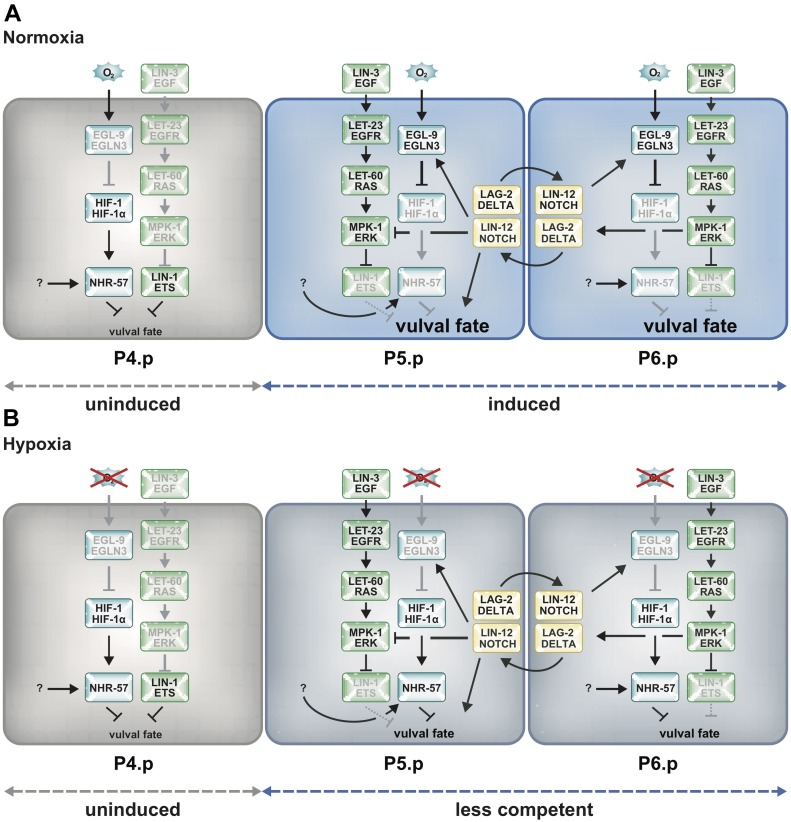
Figure 5. EGL-9 inhibits the HIF-1 target NHR-57 from reducing RAS/MAPK signaling through a DELTA/NOTCH-induced negative feedback loop.
(A) Model illustrating the cross-talk of the hypoxia-response, DELTA/NOTCH, and RAS/MAPK pathways at normoxia. At the onset of VI, before a distinction between 1° and 2° VPCs is made, lateral DELTA/NOTCH signaling between the proximal VPCs induces EGL-9 expression to maintain low HIF-1 and NHR-57 levels, thereby keeping the VPCs competent to respond to RAS/MAPK signaling. RAS/MAPK signaling, in turn, promotes the expression of the DELTA family NOTCH ligands. Distal VPCs lose their competence because of higher NHR-57 levels and adopt the 3° fate. Thereafter, NOTCH signaling directly induces the 2° fate and inhibits RAS/MAPK signaling in P5.p and P7.p. (B) Under hypoxia, the inhibition of HIF-1 and NHR-57 by EGL-9 is reduced because of the lack of oxygen and vulval fate acquisition is compromised. An as-of-yet unidentified factor activates NHR-57 during hypoxia independently of HIF-1.