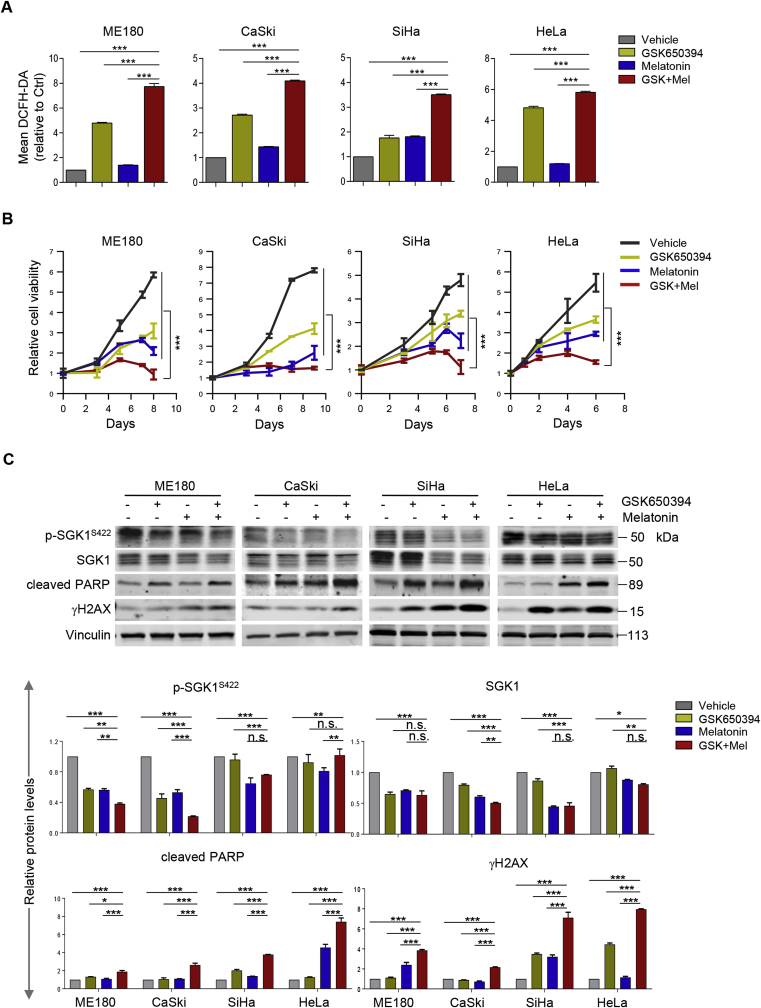
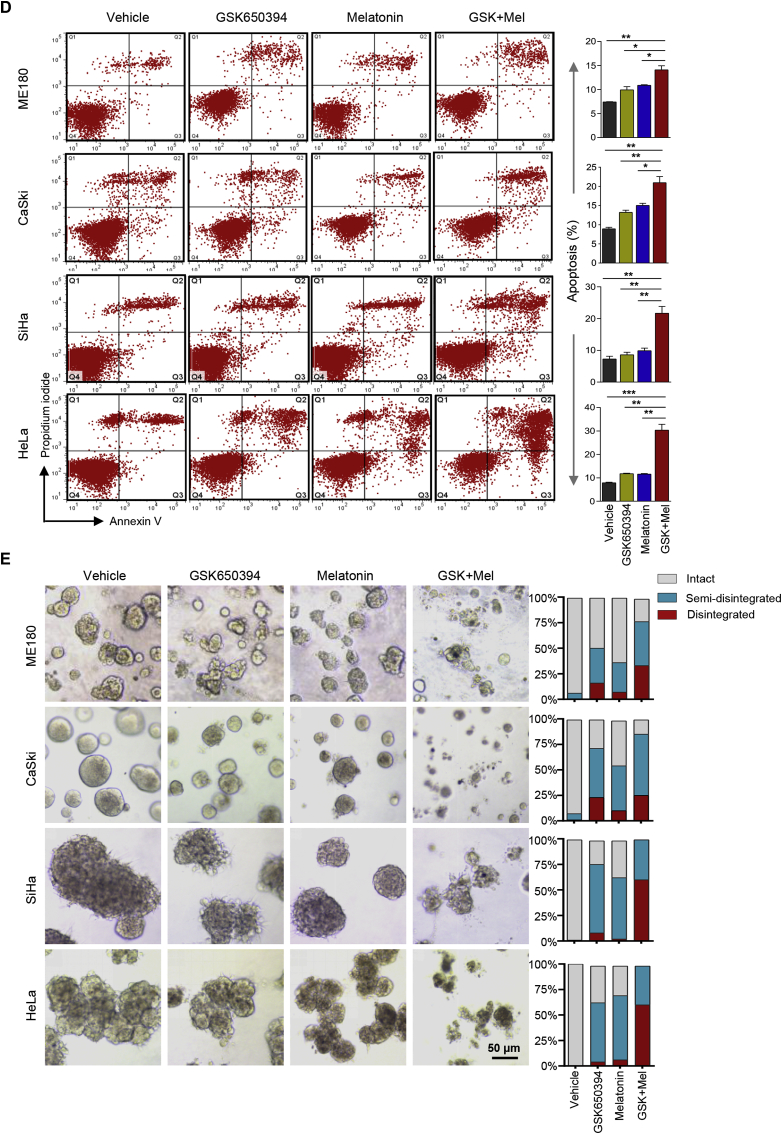
Fig. 5.
SGK1 inhibition synergizes with melatonin to induce ROS-mediated apoptosis and cytotoxicity. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of ROS levels in cervical cancer cells treated with GSK650394 and melatonin, either alone or a combination of both for 48 h. Of note, CaSki and ME180 cells were treated with 2.5 μM GSK650394 and/or 1 mM melatonin; SiHa and HeLa cells were treated with 5 μM GSK650394 and/or 2 mM melatonin. (B) Long-term cell viability was measured by crystal violet assay for cells treated as in (A). (C) Western blot analysis of proteins in cells treated as in (A). Vinculin was used as a loading control. The quantification of protein abundance is shown. (D) Apoptosis levels in cells as in (A) were determined by Annexin V/PI staining assays. Quantification for three independent experiments is shown. (E) Cervical cancer cell lines were cultured in 3D Matrigel and treated with GSK650394 and melatonin, either alone or in combination. Representative images and Quantification of scored structures (intact, semi-disintegrated and disintegrated) are shown. Scale bars, 50 μm. n. s., not significant. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 (Student's t-test). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)