Figure 5.
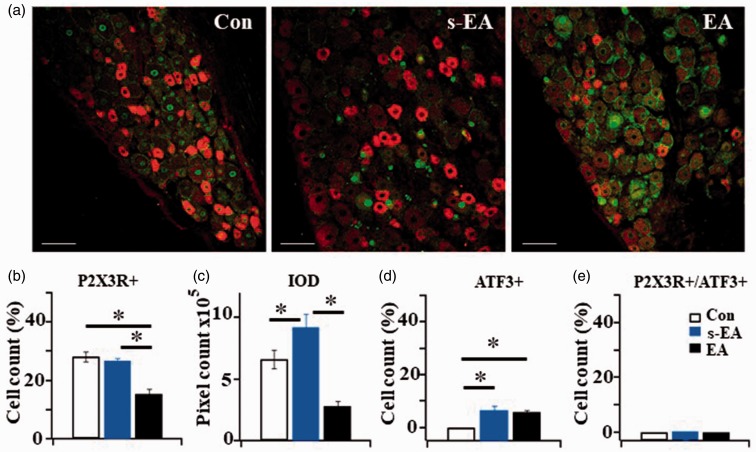
The effect of immunohistochemical study of P2X3R-ir and ATF3-ir expression in L4 DRG neurons. (a) P2X3R-ir (red) + ATF3-ir (green) double labeled DRG neurons in Control (Con), SNL+ s-EA (s-EA) and SNL+EA (EA) rats. Bar =100 µm. (b) Percentages of P2X3R+ expressing neurons in Control and SNL+ s-EA rats were similar (28.24 ± 1.69% in Con vs. 26.83 ± 0.9% in s-EA rats), The percentage of P2X3R+ neurons in SNL+ EA rats was significantly reduced (15.37 ± 1.75%). (c) Integrated optical density measured in SNL+s-EA rats ((9.21 ± 1.08) × 105) was higher than that in control rats ((6.64 ± 0.75) ×105) and much reduced ((2.81 ± 0.39) × 105) in SNL+EA rats. (d) The percentage of ATF+ neurons in SNL+ s-EA and in SNL+EA rats were not significantly different (6.7 ± 1.7 vs. 6.1 ± 0.6%, P > 0.05). Both were higher than control rats (0%). (e) Almost no P2X3+/ATF3+ neurons were expressed in the three rat groups. Thus, all of the P2X3R+ were expressed in un-injured neurons (Con: n = 7, SNL+ s-EA: n = 3, SNL+EA: n = 3). *P < 0.01. EA: electroacupuncture; ATF3: activating transcription factor 3; IOD: integrated optical density.