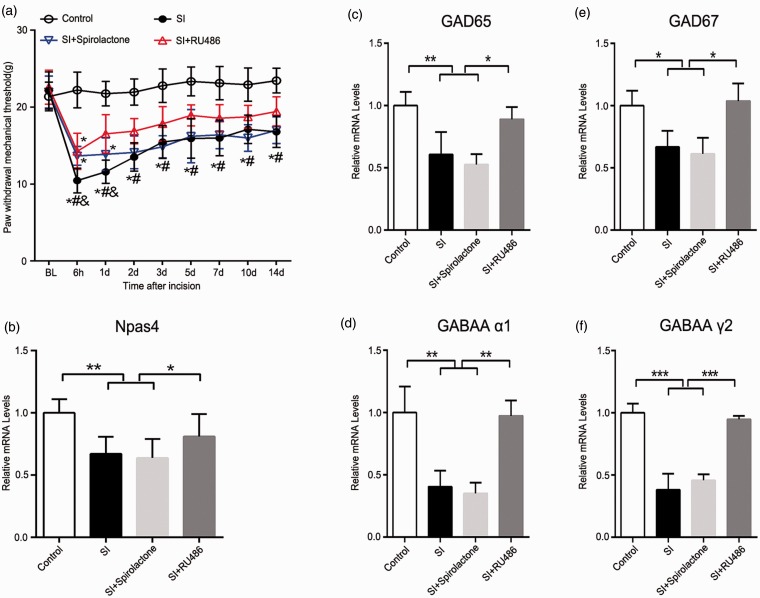
Figure 4.
Effects of RU486 and spironolactone on pain behavior, Npas4, and GABAergic markers postoperatively in SPS rats. (a) The PWMT in response to Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer of the right hind paw was measured at 24 h prior to drug or vehicle injection (baseline) and at 6 h to 14 days after incisional surgery. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA, *p < 0.05 versus control group; #p< 0.05 versus SI + RU486 group; &p < 0.05 versus SI + spironolactone group (n = 8). (b) After drug or vehicle treatment, the lumbar spinal cord was homogenized on the 14th day after incision, and Npas4 mRNA level was analyzed. (c) to (f) Quantitative RT-PCR performed to detect the mRNA in spinal cord of rats treated with RU486 or spironolactone before SPS, and sections were corresponded to GAD65, GAD67, GABAA receptor subunit α1 and γ2, respectively (n = 4). Data are presented as mean ± SD, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p < 0.05; statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni test. SPS: single prolonged stress; Npas4: neuronal PAS domain protein 4; SI: SPS + incision; PWMT: paw withdrawal mechanical threshold; ANOVA: analysis of variance; RT-PCR: real-time polymerase chain reaction.