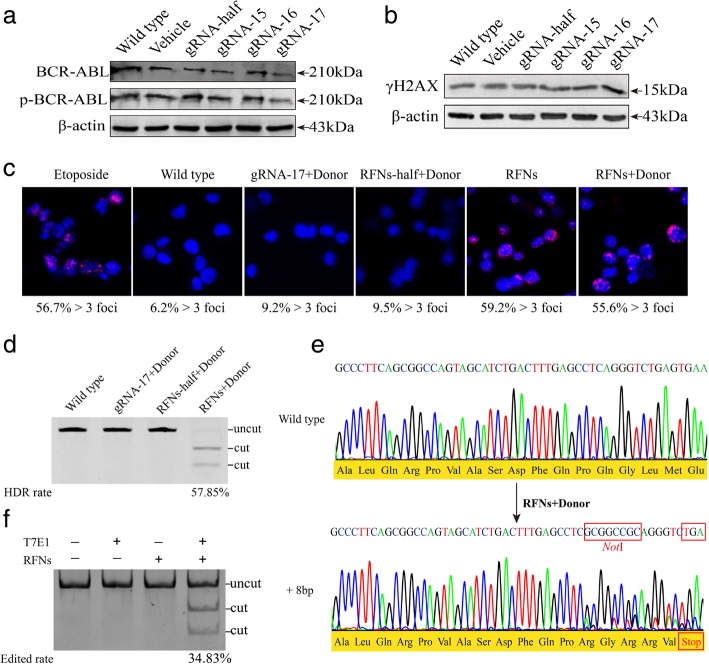
Fig. 2.
RFNs induce gene modification of bcr-abl. a Detection of BCR-ABL expression by western blot. Vehicle or each gRNA combined FokI-dCas9 plus donor were co-transfected into K562 cells. b Examination of the amount of γH2AX by western blot. K562 cells were transfected with vehicle or each gRNA guided FokI-dCas9 plus donor. c DSBs induced by RFNs were detected with 53BP1 immunostaining. Etoposide treated K562 cells were adopted as positive control and wild type K562 cells were used as negative control. Different groups of plasmids transfected K562 cells were harvested after 60 h of treatment. Foci that form more than 3 in cells were considered to be 53BP1 positive and the positive rates were shown beneath each panel. d The HDR rate of RFNs plus donor on bcr-abl was detected by NotI digestion. The “uncut” indicated the location of pcr fragment of wild type and “cut” showed the location of digested fragment by NotI restriction enzyme. e Predicted HDR was verified by Sanger sequencing. The sequence of RFNs plus donor treated cells was analyzed with in silico analysis. Result showed the NotI sequence was inserted into bcr-abl and a TGA stop codon was generated downstream of the cleavage site. f The edited rate by RFNs was detected via T7E1 assay. The “cut” bands indicated occur of “indels”