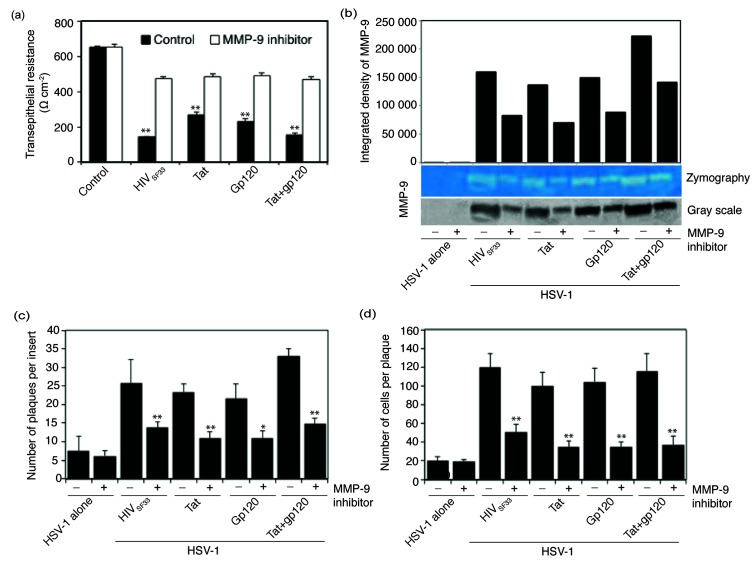
Fig. 6.
HIV-induced activation of MMP-9 is directly involved in cell-to-cell spread of HSV-1. (a and b) Polarized tonsil epithelial cells were exposed to cell-free HIV-1SF33 virions and tat and/or gp120 for 5 days in the presence of MMP-9 inhibitor I. Control cells were treated with DMSO at the same concentration as MMP-9 inhibitor I in treated cells. On day 5 the TER of polarized cells was measured (a). The culture medium of cells from panel (a) was collected and examined for MMP-9 activity by gelatine zymograpy. For quantitative analysis, gelatine zymograpy was converted to greyscale mode and the integrated density of protein bands was measured using ImageJ software (b). (c and d) Polarized epithelial cells exposed to HIV and tat and/or gp120 were infected with HSV-1 from the basolateral surface and incubated for 3 days in the presence or absence of MMP-9. Results are presented as the average number of plaques per insert (c) or the average number of infected cells per plaque (d). Error bars indicate sem (n=3). *P<0.005, **P<0.001, all compared to the control group. Two independent experiments showed similar results.