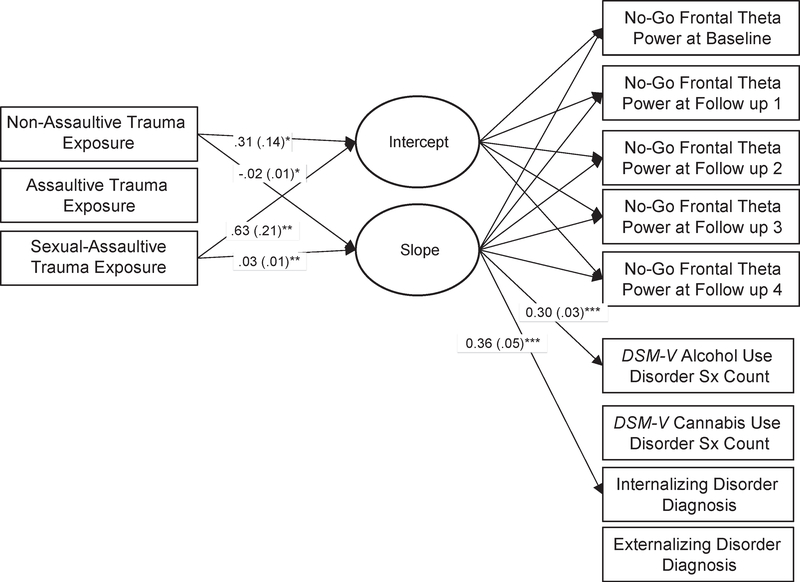
FIGURE 1.
Effects of Early Trauma Exposure on No-Go Frontal Theta Power From Baseline Through Follow-Up 4 and Associations With Substance Use Disorder and Psychopathology
Note: Parameter estimates (and standard errors) are displayed only for statistically significant pathways. Not pictured, but also included in this model, are the following covariates: gender, race/ethnicity, age, alcohol use and cannabis use, and parental alcohol use disorder. Internalizing psychopathology count scores included DSM-IV lifetime symptoms for major depressive disorder, panic disorder, social phobia, and an additional item—suicidal ideation. Externalizing psychopathology count scores included conduct disorder and oppositional defiant disorder symptoms. Data from each individual’s most recent interview were used. Sx = symptom.
*p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001.