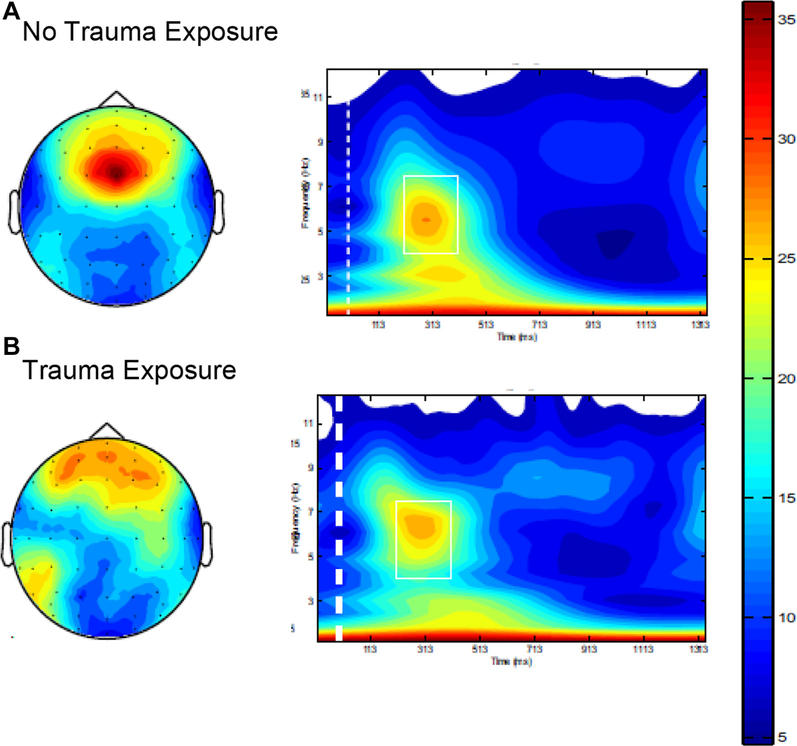
FIGURE 3.
No-Go Frontal Theta by Early Sexual Assaultive Trauma Exposure
Note: This figure depicts differences in frontal theta no-go power values at baseline observed in participants who (A) were not exposed and (B) were exposed to sexual trauma before 10 years of age. Note the more focused frontal topography and more efficient neural synchronization (ie, higher theta event-related oscillation power values) during response inhibition (no-go condition of go/no-go task) in participants who were not exposed to trauma. In contrast, the frontal topography indicates a less efficient neural synchronization (ie, lower event-related oscillation power values) during response inhibition (no-go condition of go/no-go task) in participants who were exposed to trauma. Please note color figures are available online.