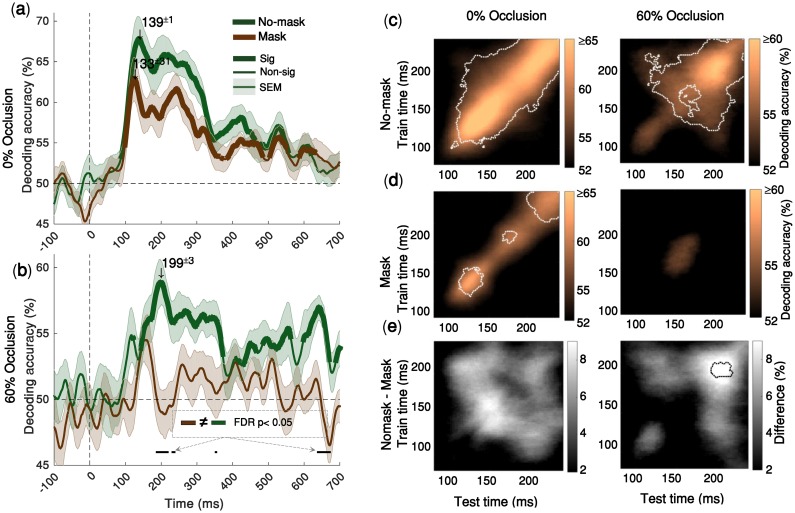
Fig 4. Backward masking significantly impairs object decoding under occlusion, but has no significant effect on object decoding under no occlusion.
(a) Time-courses of the average pairwise decoding accuracies under no-occlusion. Thicker lines indicate significant time-points (right-sided signrank test, FDR corrected across time, p < 0.05). Shaded error bars indicate SEM (standard error of the mean). Downward pointing arrows indicate peak decoding accuracies. There is no significant difference between decoding time-courses for mask and no-mask trials, under no-occlusion (b) Time-courses of the average pairwise decoding under 60% occlusion (for 80% occlusion see S5 Fig). Under occlusion, the decoding onset latency for the no-mask trials is 123±15ms, with its peak decoding accuracy at 199±3ms; whereas the time-course for the masked trials does not reach statistical significance, demonstrating that backward masking significantly impairs object recognition under occlusion. Black horizontal lines below the curves show the time-points at which the two decoding curves are significantly different. This is particularly evident around the peak latency of the no-mask trials [from 185ms to 237ms]. (c, d) Time-time decoding matrices of 60% occluded and (0%) un-occluded objects with and without backward masking. Horizontal axes indicate testing times and the vertical axes indicate training times. Color bars show percent of decoding accuracies. Please note that in the time-time decoding matrices, the color bar ranges for 0% occlusion and 60% occlusion are different. Significantly above chance decoding accuracies, are surrounded by the white dashed contour lines (right-sided signrank test, FDR corrected across the whole 801x801 decoding matrix, p < 0.05). (f) Difference between time-time decoding matrices with and without backward masking. Statistically significant differences are surrounded by the black dotted contours (right-sided signrank test, FDR corrected across time at p < 0.05). There are significant differences between mask and no-mask only under occlusion.