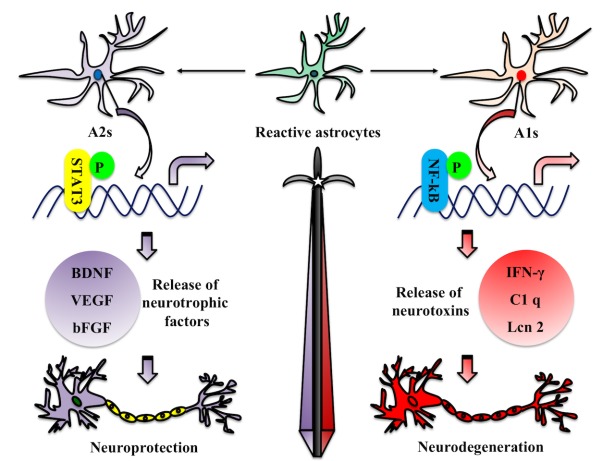
Figure 2. Roles of reactive astrocytes in the process of neuroinflammation or brain injury.
Neuroinflammation mainly induces the formation of A1 reactive astrocytes (A1s), which exhibit differential expression of astrocytic receptors, transporters, transmitters, as well as the changes of protein release and inflammatory factors. These changes may result in loss of neuroprotective function or neurological toxicity, a collapse of the brain-blood barrier and an increase in inflammation of the brain, which eventually results in deaths of neurons and causes neurodegenerative diseases. While A1s can upregulate many genes that are destructive to synapses, A2 reactive astrocytes (A2s) can upregulate many neurotrophic factors promoting the survival of neurons.