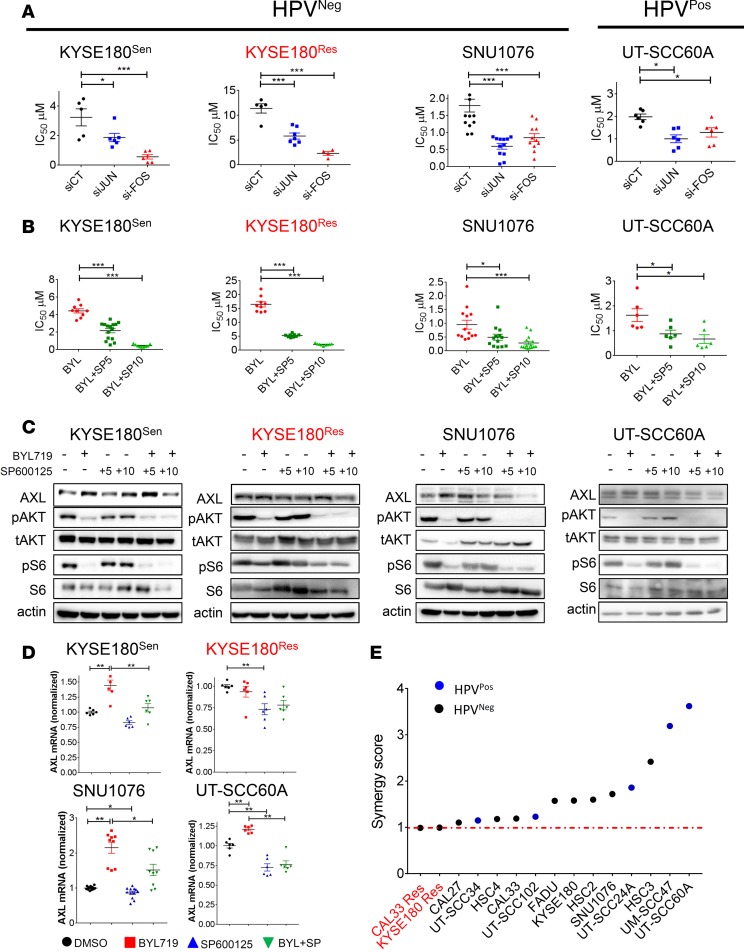
Figure 4. Silencing of c-JUN and c-FOS or blocking JNK sensitizes HNSCC and ESCC cells to BYL719 in vitro.
(A) Viability was assessed in cell lines treated with escalating doses of BYL719 for 4 days. Analysis of BYL719 IC50 values in HNSCC and ESCC cells following transfection with siRNAs to silence c-JUN and c-FOS expression (n > 6). (B) Viability was assessed in cell lines treated with BYL719 and SP600125 for 4 days. Analysis of BYL719 IC50 values following JNK inhibition with SP600125 (5 and 10 μM) in HNSCC and ESCC cells (n > 6). (C) WB analysis showing AXL level and AKT/mTOR pathway activation in HNSCC and ESCC cells treated with BYL719 (2 μM), SP600125 (5 and 10 μM), and the combination therapy for 24 hours. (D) qPCR analysis of AXL mRNA levels in cells treated as in with BYL719 (2 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), and combination for 24 hours (n > 6). (E) Viability was assessed in cell lines treated with escalating doses of BYL719 and SP600125 for 4 days. Synergy test for the interaction between BYL719 and SP600125. The synergy test was analyzed using Chalice software (Horizon), and a synergy score was extracted. All WB analysis was assessed in 2–3 independent experiments. All viability experiments were assessed in 2–3 independent experiments. All qPCR experiments were assessed in 2–3 independent experiments. One-way ANOVA P values are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.