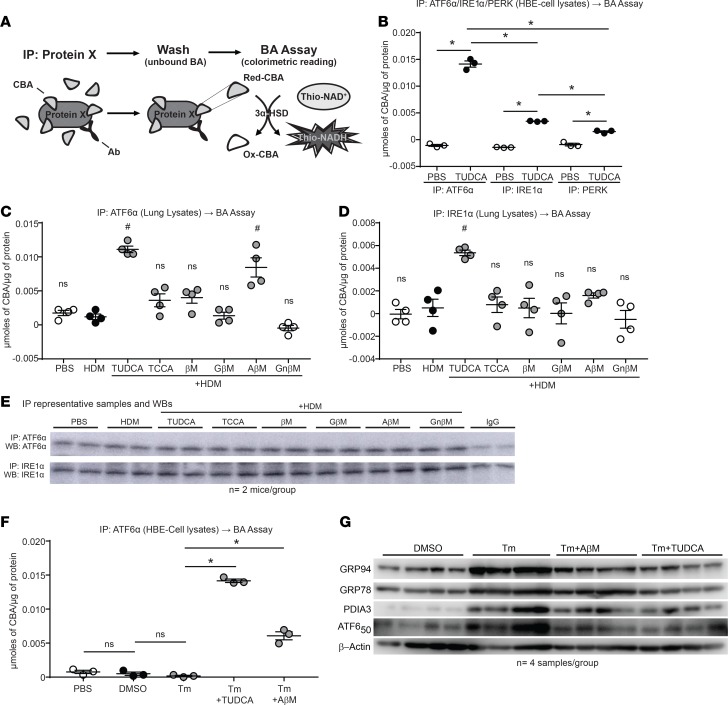
Figure 9. CBAs inhibit the UPR and airway inflammation via direct binding of the UPR transducer ATF6α.
(A) Outline of the IP and subsequent bile acid assay protocol. (B) Bile acid assay performed on ATF6α, PERK, and IRE1α IP from HBE cells stimulated with or without TUDCA. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05; n = 3 samples per group from 1 experiment. (C and D) Bile acid assay performed on ATF6α and IRE1α IP from lung lysates of untreated and CBA/UBA–treated mice challenged with HDM. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. #P < 0.05 vs. both PBS and HDM control groups; n = 4 mice per group from 2 experiments. (E) Representative Western blots from IPs of ATF6α and IRE1α from mouse lung lysates. (F) IP and subsequent bile acid assay from cell lysates of untreated and TUDCA/AβM–treated cells challenged with Tm. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05; n = 3 samples per group from 1 experiment. (G) Western blots for UPR markers from cell lysates of untreated and TUDCA/AβM–treated cells challenged with Tm. IP, immunoprecipitation; UBA, unconjugated bile acid; CBA, conjugated bile acid; Ab, antibody; 3α-HSD, 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; Red, reduced; Ox, Oxidized; ns, not significant. Error bars represent ± SEM.