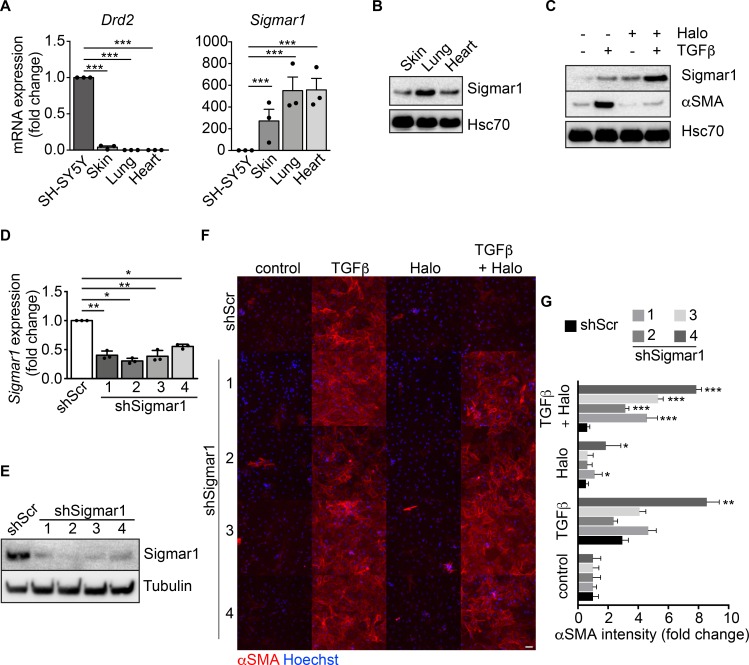
Figure 3. Sigmar1 mediates haloperidol activity in fibroblasts.
(A) Relative mRNA expression of dopamine receptor D2 (Drd2) and sigma receptor 1 (Sigmar1) in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells, skin, lung, and heart fibroblasts (n = 3/gp). (B) Western blot for Sigmar1 in skin, lung and cardiac fibroblasts. Hsc70 is shown as loading control run in parallel with Sigmar1. (C) Western blot showing the expression of αSMA and Sigmar1 in cardiac fibroblasts upon treatment with TGF-β, haloperidol, or their combination. Hsc70 is shown as loading control run in parallel. (D) Quantitative real-time PCR showing the level of Sigmar1 expression upon delivery of 4 specific shRNAs (shSigmar1–4) in primary adult cardiac fibroblasts (n = 3/gp). A scrambled sequence of shSigmar1-1 was used as a control. (E) Western blot showing the expression level of Sigmar1 upon delivery of 4 specific shRNAs (shSigmar1–4) in primary adult cardiac fibroblasts, using the scrambled sequence of shSigmar1-1 as a control. Tubulin is used as loading control. (F) Representative images of αSMA staining (red) in cardiac fibroblasts upon Sigmar1 silencing using the 4 shRNAs and treatment with TGF-β, haloperidol, or their combination. Nuclei are stained blue with Hoechst. Scale bar: 100 μm. (G) Quantification of αSMA mean intensity in cardiac fibroblasts upon Sigmar1 silencing using the 4 shRNAs and treatment with TGF-β, haloperidol, or their combination (n = 3/gp). Values in A, D, and G are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (relative to control in J) by unpaired t test with Welch’s correction.