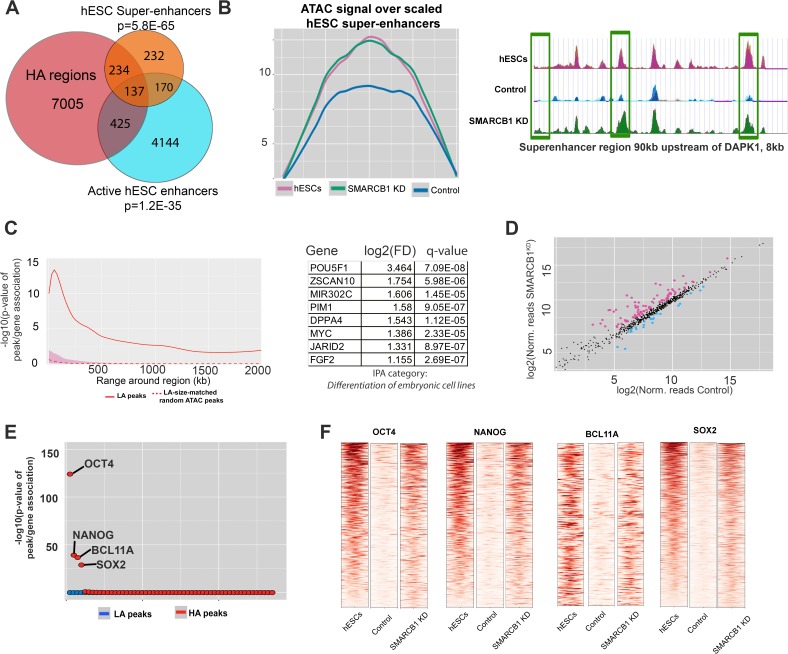
Figure 5. hESC chromatin landscape resists silencing during neural induction protocol in SMARCB1 KD cells.
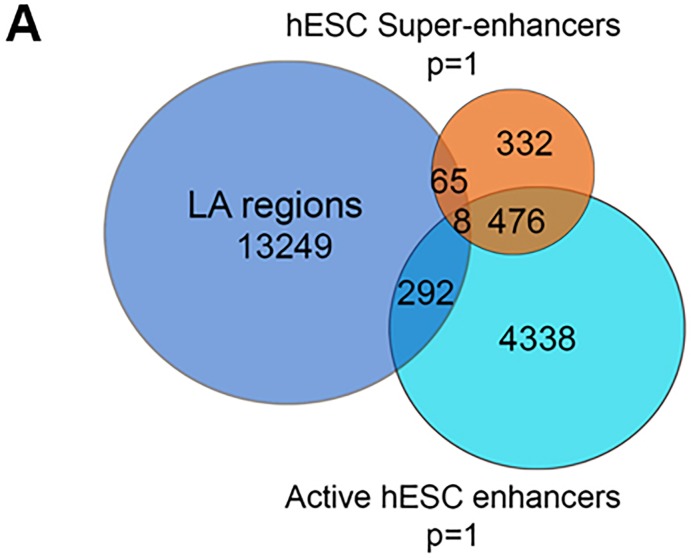
(A) Venn diagram showing the overlap between higher accessibility peaks in SMARCB1 KD cells subjected to the neural induction protocol and hESC enhancers and super-enhancers. The degree of significance of the overlap is given. (B) Left: Accessibility signals over hESC super-enhancers for steady state hESCs as well as control and SMARCB1 KD cells subjected to neural induction protocol. Right: Track showing normalized accessibility signals for steady state hESCs as well as control and SMARCB1 KD cells subjected to neural induction protocol over an 8 kb portion of a SE near the DAPK1 locus. Differentially accessible peaks are marked with green boxes. (C) Left: Significance of the association between peaks with higher accessibility in hESC super-enhancers and differentially expressed genes by RNAseq over a range of 2 Mb. The red shaded region reflects the 5–95% confidence interval (CI) for the significance of the association between differentially expressed genes and 1000x sets of randomly selected ATAC peaks that were matched in size and number to the set of higher accessibility ATAC peaks in hESC super-enhancers. The dotted line indicates the median of the random peak set-based significance range. Right: Differentially affected genes within 500 kB of an hESC SE with at least one higher accessibility region in SMARCB1 KD cells following the neural induction protocol. (D) Scatterplot showing the number of normalized RNAseq reads over hESC super-enhancers in both control and SMARCB1 KD cells subjected to a neural induction protocol. Pink dots indicate regions with significantly higher levels of RNA, and blue dots indicate regions with lower levels of transcription. (E) Dot plots indicating the significance of intersection between SMARCB1 KD lower/higher accessibility in the neural induction experiments and hESC transcription factor binding sites. The plot is ordered with the ChIPseq peaks most significantly associated with higher accessibility on the left. (F) Heat map indicating the significance of overlap between hESC ChIPseq peaks and higher/lower accessibility in SMARCB1 KD cells following the neural induction protocol. Darker colors indicate a higher degree of significance. Right: Normalized accessibility signals over hESC binding sites for OCT4, NANOG, BCL11A, and SOX2 for steady state hESCs as well as control and SMARCB1 KD cells subjected to the neural induction protocol.