Figure 2. Cysteine-832 mediates oxidative stress-induced inhibition of Ire1.
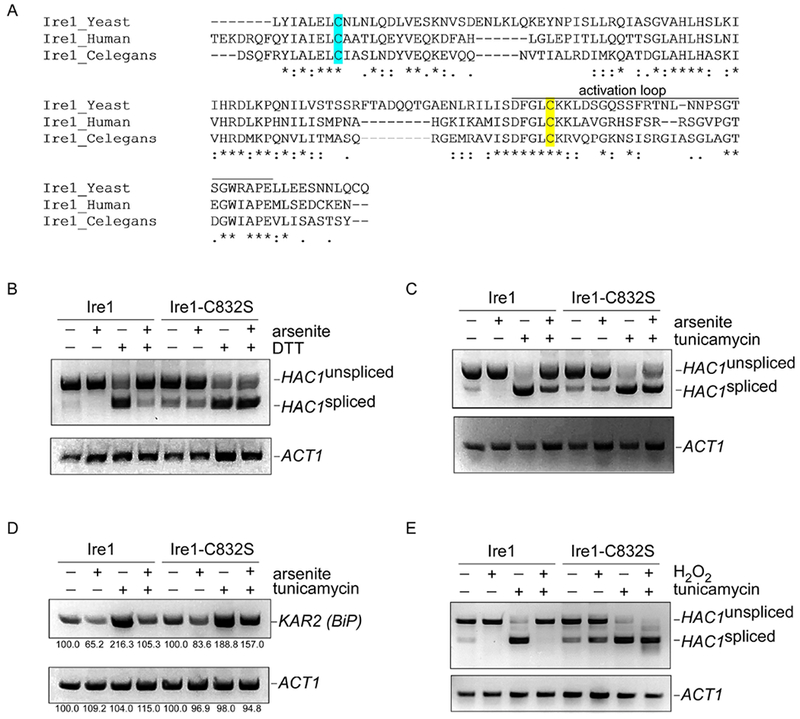
A) Sequence alignment of the critical region of Ire1 from S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, and humans. Cysteine-832 is highlighted in yellow. Cysteine-748 is highlighted in cyan. Asterisks, identical residues; double dots, highly similar residues; single dots, similar residues.
B-C) The ire1-C832S mutant is refractory to arsenic-induced inhibition of HAC1 splicing, as determined by RT-PCR. HAC1 splicing was induced by either DTT (1.5 mM; panel B) or tunicamycin (5 μg/ml; panel C). Arsenite was used at 1 mM. Treatment was for one hour. Lower panels, ACT1 controls.
D) The ire1-C832S mutant is refractory to arsenic-induced inhibition of transcription of the HAC1 target KAR2, as determined by RT-PCR. Treatment was with tunicamycin (5 μg/ml) and/or arsenite (1 mM) for one hour. Lower panel, ACT1 control. Images were quantitated using NIH Image J, and the relative expression of KAR2 and PGK1 is indicated as a percentage of the respective untreated control.
E) The ire1-C832S mutant is refractory to hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of HAC1 splicing, as determined by RT-PCR. HAC1 splicing was induced by tunicamycin (5 μg/ml). Hydrogen peroxide was used at 5 mM. Chemical treatment was for one hour. Lower panel, ACT1 control.
