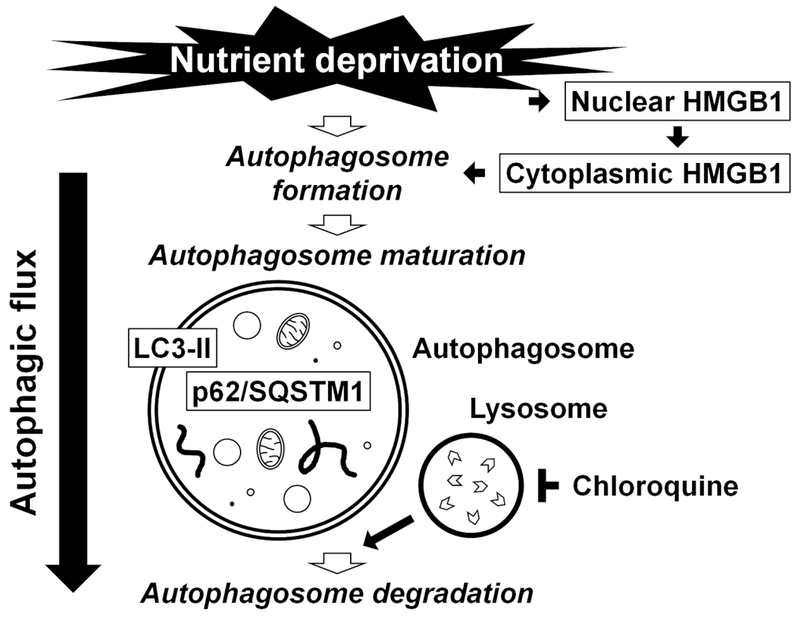
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration summarizing the process of autophagy examined in this study.
Under nutrient deprivation, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, resulting in the initiation of the autophagosome formation. The autophagosome maturation is driven by the conjugation of phosphatidylethanolamine with light chain 3 (LC3), leading to the formation of its autophagosome membrane-bound form, LC3-II. The p62/sequestosome 1 (p62/SQSTM1) and p62/SQSTM1-bound polyubiquitinated proteins become incorporated into completed autophagosomes. The completed autophagosome fuses with the lysosome (inhibited by chloroquine), the enclosed cargo is degraded, and its constituents are released and reutilized. Understanding of autophagy requires monitoring this dynamic, multi-step process of autophagic flux.