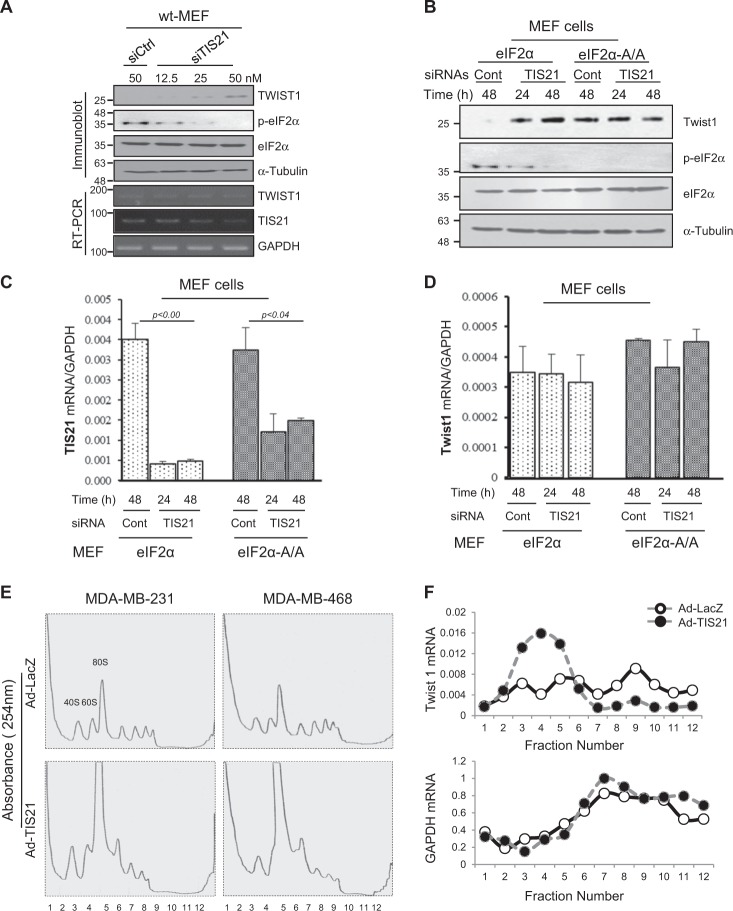
Fig. 5. BTG2/TIS21-induced Twist1 loss is associated with the failure of polysome formation.
a Twist1 expression was significantly induced by knockdown of endogenous BTG2/TIS21 expression. To confirm the effect of BTG2/TIS21 on the Twist1 protein loss, TIS21/BTG2 expression in the wild-type MEF was removed by transfection with siTIS21 (12.5~50 nM) for 2 days and then analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Twist1 antibody. The induction of Twist1 expression appeared in the siTIS21-dependent manner, compared with that in the control. In the same cells, p-eIF2α level maintained in the siControl-transfected cells was significantly reduced by knockdown of BTG2/TIS21 expression. Total eIF2α levels remained unaltered. α-Tubulin served as a loading control. RT-PCR analysis showed that Twist1 mRNA level was unchanged. TIS21 knockdown was analyzed by RT-PCR and GAPDH served as a control. b Wild-type MEF cells overexpressed with either eIF2α or eIF2α-A/A (S51A/S51A) mutant were transfected with siTIS21-RNAs (50 nM) and siControl-RNAs (50 nM), and the cells were subjected to immunoblot assay in 24 and 48 h of the transfection. Knockdown of BTG2/TIS21 expression by siTIS21 significantly induced Twist1 expression compared with that in the siControl (lanes 2 and 3 vs. lane 1); however, Twist1 expression was consistently high in the MEF cells with eIF2α-A/A mutant expresser (lanes 5 and 6 vs. lane 4). The phosphorylation of eIF2α completely disappeared by the knockdown of BTG2/TIS21 expression for 48 h, suggesting that BTG2/TIS21 expression might maintain the p-eIF2α level that inhibits translation of Twist1. c, d Real-time qPCR analyses revealing mRNA expressions of BTG2/TIS21 (c) and Twist1 (d) in the MEF cells transfected with wild-type and mutant eIF2α. Transfection of MEF with siTIS21 markedly reduced BTG2/TIS21 expression; however, Twist1 transcription was not significantly changed by BTG2/TIS21 knockdown. Relative expressions were presented based on that of GAPDH. e Polysome profiling assay; to assess a general translational control by BTG2/TIS21 gene, TNBC cells transduced with either Ad-LacZ or Ad-TIS21 for 48 h were subjected to polysome profiling analysis. Polysome formation in the BTG2/TIS21 expresser was collapsed after a huge peak of the 80S monomer, whereas the profile was well maintained in the LacZ control. Numbers in X axis (1–12) indicate fractions collected up to 500 μL per each tube. f Real-time PCR analysis; to analyze abundance of the Twist1 mRNAs in each fraction, real-time PCR analysis was performed. The amount of Twist1 mRNA was higher in the 2–5 fractions of the BTG2/TIS21 expresser; however, it was much less in the 6–12 fractions compared with those in the LacZ expresser. In contrast, levels of GAPDH mRNA were similar between the LacZ and BTG2/TIS21 expressers in each fraction. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. All data are expressed as mean ± SD after two independent experiments