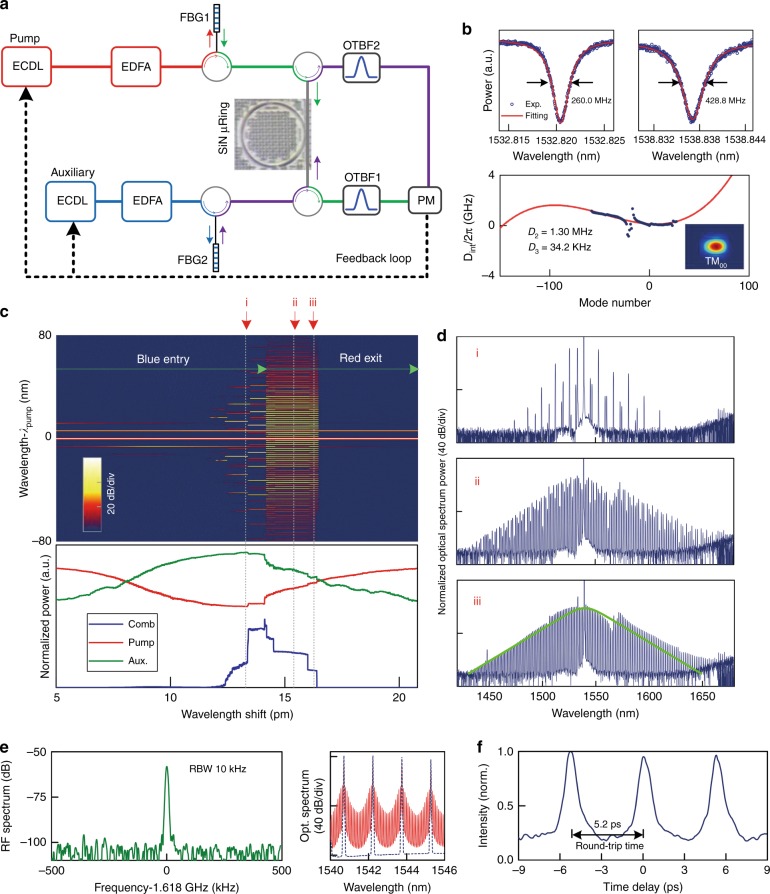
Fig. 1. Auxiliary-assisted frequency comb and stable DKS generation with pump-cavity blue-sided entrance.
a Schematic for the experimental setup. Two ECDLs (one used as the auxiliary laser and the other as the pump laser) are amplified and launched into a Si3N4 microring resonator from opposite directions. The auxiliary laser is preset in the blue-detuning regime of one cavity mode, which maintains the cavity thermal stability and escorts the pump to stably traverse an entire cavity linewidth. EDFA: erbium doped fiber amplifier; FBG: fiber Bragg grating; PM: power meter; OTBF: optical tunable bandpass filter. b Upper panel: measured linewidth for two cavity resonances centered around 1532.8 nm and 1538.8 nm, from where the auxiliary and pump lasers enter the cavity. The two resonances have a loaded Qs of ≈750,000 and 450,000, respectively. Lower panel: measured (blue dots) and FDTD simulated (red solid line) dispersion Dint = ωμ ω0 μD1 of the fundamental TM00 mode of the microcavity. Here, ω0 is the angular frequency of the pumped cavity mode, ωμ is the angular frequency of the μ-th cavity mode relative to ω0, and D1 is the FSR measured at ω0. The inset shows the simulated mode profile for mode TM00. c Measured frequency comb spectrum (upper) and power evolutions (lower) as a 1.0 W c.w. pump laser adiabatically scans from the blue- to red-detuning regimes of a cavity mode. The pump scan is conducted with increasing step wavelength, with a 40 fm (5 MHz) step size and a delay of 0.1 s after each step. The auxiliary laser is operated at similar intensities. The pump and auxiliary laser dynamics counter-balance thermal influences on the microcavity, resulting in a pump power evolution with little thermal hysteresis. d Optical spectral snapshots of the generated Kerr frequency comb with the (i) low-noise subcombs state, (ii) multiple DKS state, and (iii) singlet DKS state. The RF spectra are consistently at the noise floor for all three comb states. e Beat note measurement of the singlet DKS frequency comb (left panel), using cross-phase-modulation sidebands to reduce the initial comb mode spacing (right panel). f SHG-based autocorrelation measurement for the singlet DKS frequency comb