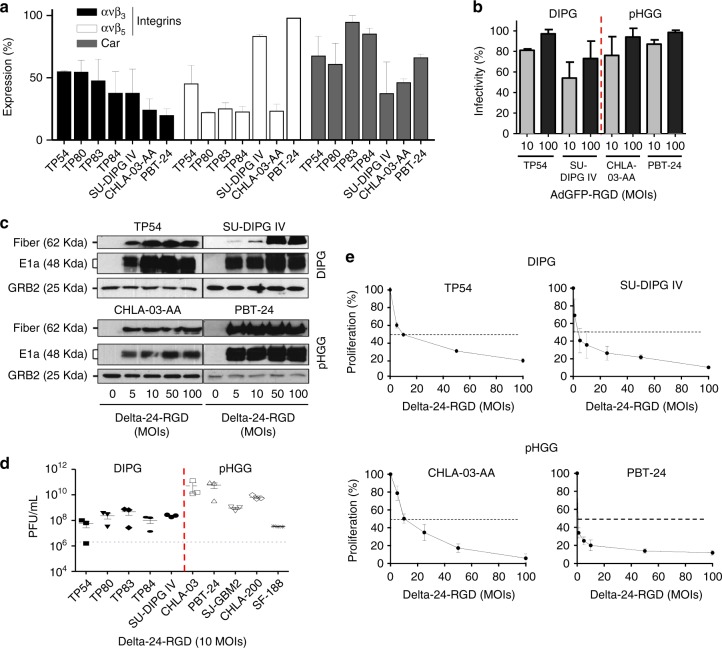
Fig. 2.
Delta-24-RGD exerts a potent oncolytic effect in DIPG and pHGG cell lines. a Flow cytometry analyses of CAR and integrin expression. DIPG and pHGG cell lines were incubated with fluorescent antibodies against ανβ3 and ανβ5 integrins and CAR. The data are shown as the relative percentage (mean ± SD) of positive expression scored among 10,000 cells. b Assessment of infectivity in DIPG and pHGG cell lines. The indicated cell lines were infected with a replication-deficient construct expressing a modified fiber knob (AdGFP-RGD). The data are shown as the relative percentage (mean ± SD) of GFP-positive cells scored among 10,000 cells per treatment group. c Assessment of viral protein expression in pHGG and DIPG cell lines infected with Delta-24-RGD by western blotting. One representative blot is shown of three independent experiments. d Quantification of Delta-24-RGD replication in the indicated cell lines. Viral titers were determined three days after infection at an MOI of 10 (106 pfu/ml) by an anti-hexon staining-based method in 293 cells and expressed as plaque-forming units (pfu) per milliliter. The dashed line indicates the input virus. The data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. e Cell proliferation analyses of Delta-24-RGD-infected DIPG and pHGG cell lines. Cell viability was assessed using MTS assays 5 days after infection. The data are shown as the percentage (mean ± SD of three independent experiments) of cells alive after infection with Delta-24-RGD at the indicated multiplicities of infection (MOIs) relative to the non-infected cells (control, equal to 100%). Source data are provided as a Source Data file