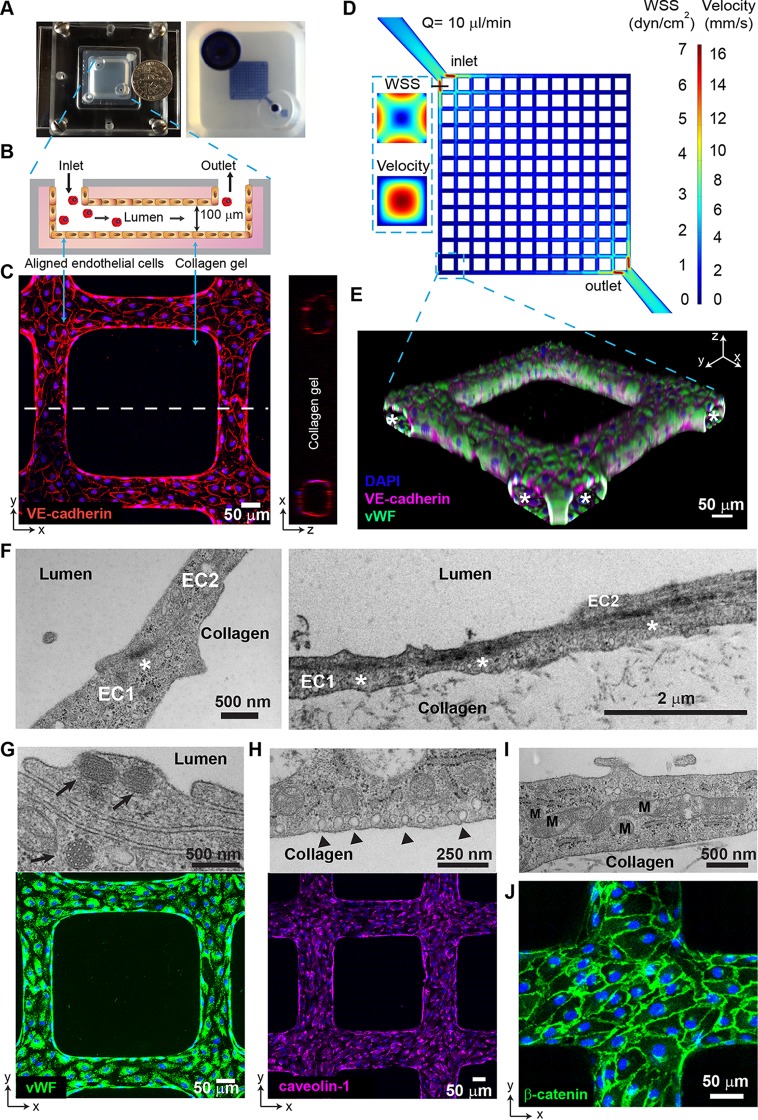
FIG 1.
Characterization of 3D brain microvessels. (A) (Left) Photo of an assembled 3D microvessel device with a dime (diameter, 17.9 mm). (Right) 3D microvessels perfused with food dye. (B) Schematic cross-sectional view of the 3D microvessels. (C) Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) z-projection of confocal sections of a 3D brain microvessel (left) and cross-sectional view (right) labeled with anti-VE-cadherin (red) and DAPI (blue). (D) Mid-plane flow velocity (z = 50 μm) and estimated WSS (z = 0 μm) distributions in the grid geometry, simulated with COMSOL prior to collagen remodeling by HBMEC (see Materials and Methods). Inlaid cross-sectional views represent the lumen at the first branch after the inlet. (E) 3D reconstruction of a grid portion. Colors indicate anti-VE-cadherin antibody (red), anti-VWF antibody (green), and DAPI (blue). Asterisk, lumen. (F) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showing endothelial junctions and focal contacts. EC1 and EC2, endothelial cells 1 and 2; asterisk, electron-dense contacts. (G) TEM showing Weibel-Palade bodies (arrows, top) and IFA z-projection of VWF (green, bottom). (H) TEM image of polarized caveolae (arrowheads, top) and IFA z-projection of caveolin-1 (magenta, bottom). (I) TEM image reveals high mitochondrial (M) content of HBMEC. (J) IFA z-projection of adherens junctions stained with anti-β-catenin antibody (green). Nuclei in panels G, H, and J were stained with DAPI (blue).