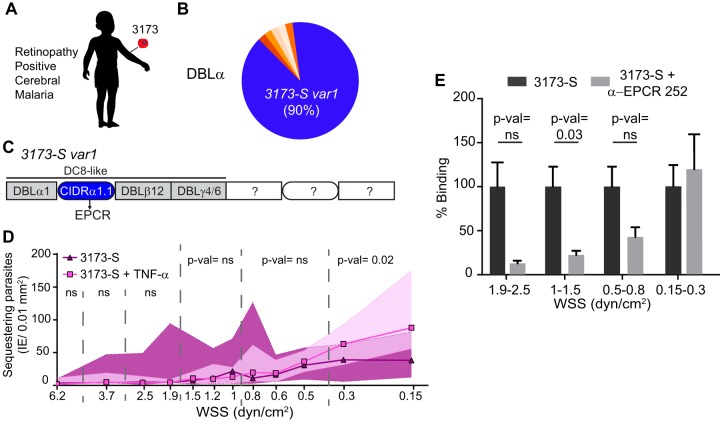
FIG 6.
Binding of a cerebral malaria isolate in 3D brain microvessels. (A) 3D microvessels were perfused by a parasite isolate (3173-S) that was cloned by limited dilution from a retinopathy-positive, cerebral malaria patient. (B) Sequencing of N-terminal DBLα tags showed that a single var gene accounts for 90% of the total amplified var transcripts. (C) Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis with var domain primers and extension of the dominant DBLα tag sequence into the flanking domains (Fig. S6) revealed that the 3173-S var1 transcript presents a DC8-like architecture predicted to bind to EPCR. (D) Binding of 3173-S (n = 5 to 6 independent biological replicates) to resting and TNF-α-activated (18 h) 3D microvessels. Dots represent median binding levels, and the colored area represents the interquartile range. (E) Percentage of binding of 3173-S in the absence or presence of anti-EPCR MAb 252 inhibitory antibody. The percentage of binding is normalized to the binding levels in the absence of treatment. Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 5 to 6 independent biological replicates). Statistical analysis of binned regions in panels D and E was determined by Mann-Whitney test.