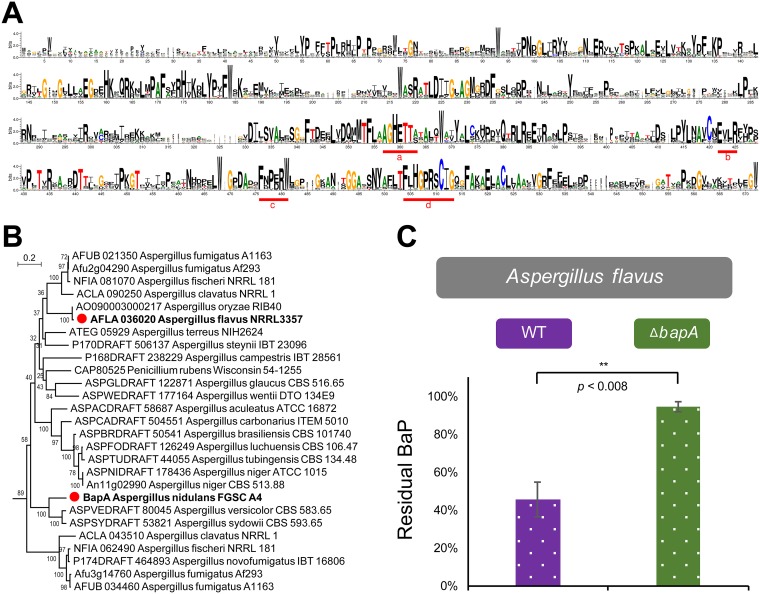
FIG 4.
The BapA CYP signature motifs, distribution of BapA in Aspergillus species, and the role of BapA in BaP degradation in A. flavus. (A) Conserved domains of the CYP617 family proteins queried from FungiDB (42) showing greater than 40% identity against the A. nidulans BapA protein (listed in Fig. S5). (B) Phylogenetic tree of the CYP617D members in Aspergillus having greater than 55% identity against the A. nidulans BapA protein. These proteins can be classified into the same subfamily, CYP617D, based on the rules of the International P450 Nomenclature Committee. For the expanded information, see Fig. S5 and Table S3. (C) Residual BaP in WT and the ΔbapA mutant of A. flavus. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and three independent ΔbapA strains were tested. **, P = 0.008.