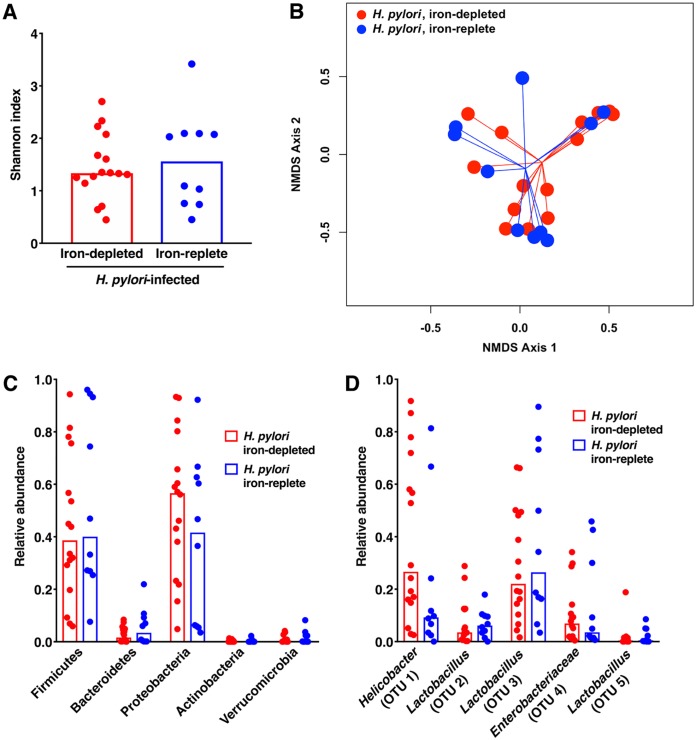
FIG 4.
Host iron levels fail to alter the diversity or composition of the gastric mucosal microbiota. Gastric tissue from uninfected gerbils or gerbils infected with wild-type H. pylori strain 7.13 maintained on either iron-depleted (n = 16) or iron-replete (n = 10) diets was harvested 6 weeks postchallenge in linear strips, extending from the squamocolumnar junction to the proximal duodenum, and then homogenized. Microbial DNA was extracted from gastric tissue and subjected to 16S rRNA gene sequencing. (A) α-Diversity of the gastric microbiota was measured by Shannon diversity metric among H. pylori-infected gerbils maintained on either iron-depleted or iron-replete diets. (B) β-Diversity of the gastric microbiota was measured by Yue and Clayton’s measure of dissimilarity and is shown in a nonmetric multidimensional scaling plot among H. pylori-infected gerbils maintained on either iron-depleted or iron-replete diets. (C) The relative abundance of phyla within in the gastric microbiota was determined among H. pylori-infected gerbils maintained on either iron-depleted or iron-replete diets. (D) Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were measured by the LDA effect size (LEfSe) algorithm among H. pylori-infected gerbils maintained on either iron-depleted or iron-replete diets.