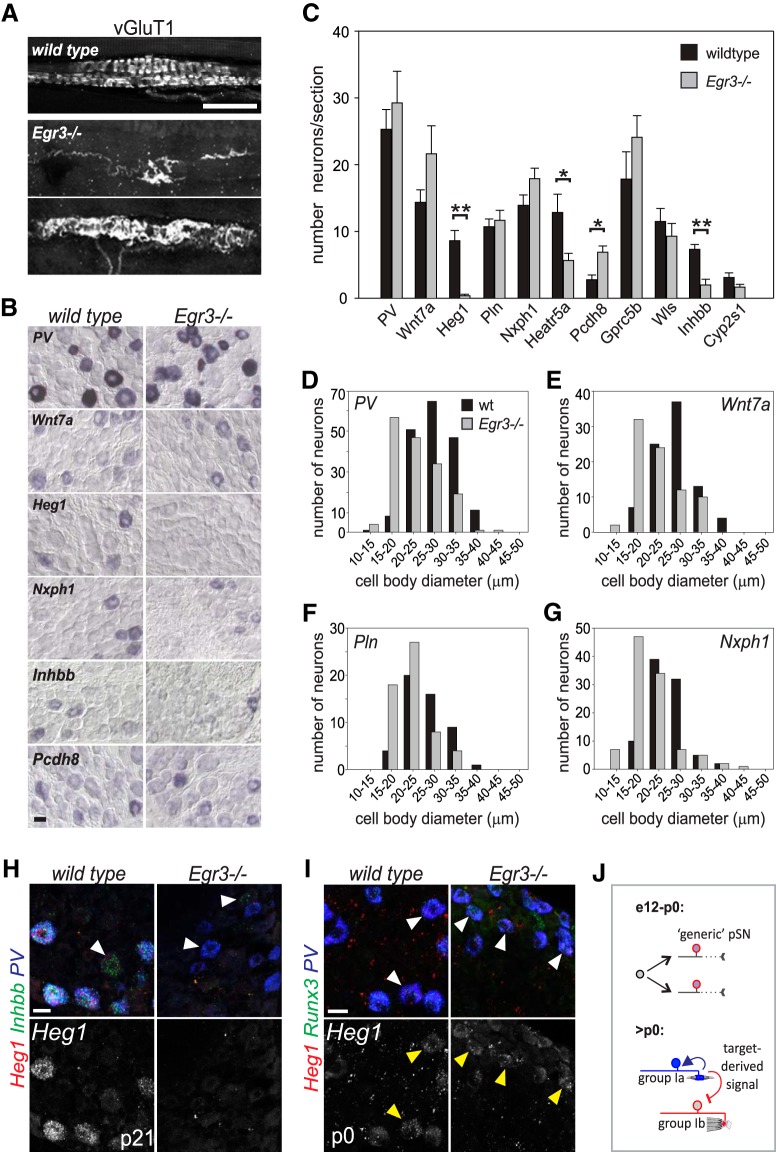
Figure 7.
Expression of pSN subtype markers depends on the presence of MS sensory end organs. A, Group Ia/II MS sensory endings in hindlimb muscle of WT and Egr3−/− mice as visualized by the expression of vGlut1. While most MS afferents retract from spindles in Egr3 mutants, a few afferents remain. Remaining afferents exhibit severely abnormal morphology. B, Expression of select candidate pSN subtype markers in WT and Egr3−/− limb level DRG at p21. C, Mean (± SEM) number of sensory neurons that express a given candidate pSN subtype marker in WT and Egr3−/− DRG sections. Quantifications performed on p21 cervical DRG and based on at least 6 sections/marker. Similar results were obtained in at least 3 mutant animals. The number of Heg1+, Heatr5a+, and Inhbb+ neurons is significantly reduced in Egr3−/− DRG (Mann–Whitney rank sum test, p < 0.001 for Heg1; t test, p = 0.017 for Heatr5a; t test, p < 0.001 for Inhbb). In contrast, the number of Pcdh8 neurons is increased in Egr3−/− DRG (t test, p = 0.003). D–G, Mean (± SEM) cell body diameter of PV (D), Wnt7a (E), Pln (F), and Nxph1 (G) neurons in WT and Egr3−/− DRG. Similar as for PV, mean cell body diameters of Wnt7a, Pln, and Nxph1 neurons are reduced in Egr3−/− mice, a consequence of a loss in the proportion of larger (25–35 μm) neurons and an increase in the proportion of smaller sized (15–25 μm) neurons (PV: 27.5 ± 0.4 μm for wt, 22.9 ± 0.4 μm for Egr3−/−; Wnt7a: 26.4 ± 0.5 μm for wt, 22.3 ± 0.6 μm for Egr3−/−; Pln: 26.0 ± 0.6 μm for wt, 22.2 ± 0.6 μm for Egr3−/−; Nxph1: 24.5 ± 0.4 μm for wt, 22.9 ± 0.4 μm for Egr3−/−; for all Mann–Whitney rank sum test, p < 0.001). H, RNAscope analysis of Heg1 and Inhbb in PV+ neurons in p21 WT and Egr3−/− lumbar DRG. Heg1 is completely absent, and Inhbb is nearly absent from PV+ neurons. White arrowhead indicates a PV neuron in which low levels of Inhbb expression remain. Yellow arrowheads indicate Inhbb expression in non-PV neurons. I, RNAscope analysis of Heg1 in PV+Rx3+ neurons in p0 WT and Egr3−/− lumbar DRG. J, Schematic depicting a possible mechanism for proprioceptor muscle afferent specification. pSNs are born without subtype identity and may innervate their target muscles in a largely naive state. Once contact is made with nascent MS or GTO receptor targets, a pSN subtype specific identity is imposed or reinforced through MS or GTO-derived signals. Scale bars: A, H, I, 20 μm; B, 50 μm. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001.