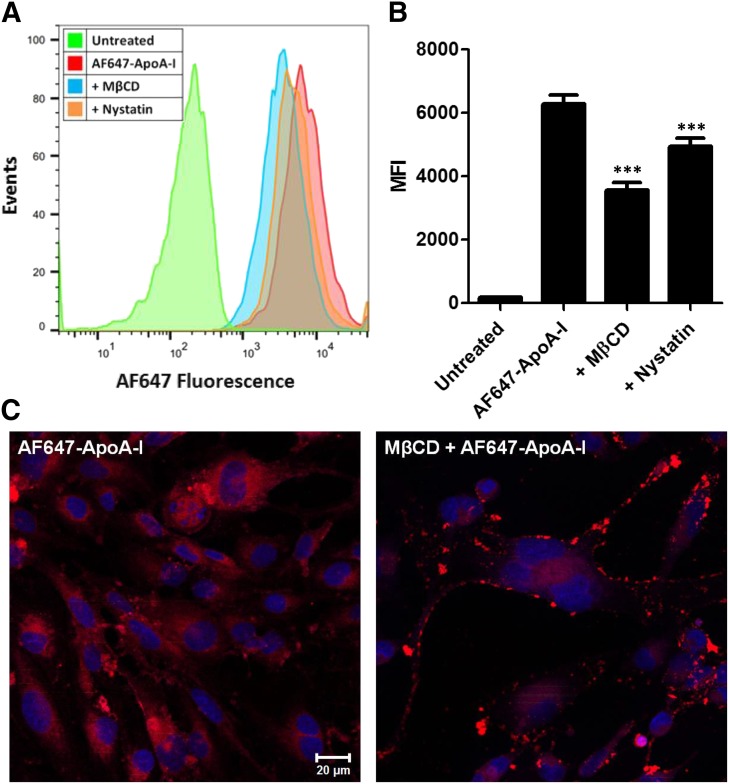
Fig. 4.
Disruption of membrane cholesterol with methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) or nystatin reduces the uptake of Alexa Fluor 647-labeled ApoA-I (AF647-ApoA-I) in hCMEC/D3 monolayers. (A) Representative flow cytometry histograms showing a decrease in the fluorescence uptake of AF647-ApoA-I (0.4 µM) after 1 hour of pretreatment with MβCD (10 mM) or Nystatin (50 µM). (B) Evaluation by flow cytometry: fluorescence uptake of AF647-ApoA-I after pretreatment with MβCD or nystatin represented as median fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± S.D. (n = 3). One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post tests showed a significant decrease in AF647-ApoA-I uptake in the MβCD or nystatin pretreated cells compared with cells treated with AF647-ApoA-I alone (***P < 0.001). (C) Laser confocal micrographs of hCMEC/D3 monolayers pretreated with MβCD show reduced intracellular accumulation of AF647-ApoA-I (right) when compared with cells treated with AF647-ApoA-I alone (left). The images are representative of two independent experiments. Red = AF647-ApoA-I; blue = DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bar, 20 µm.