Figure 7.
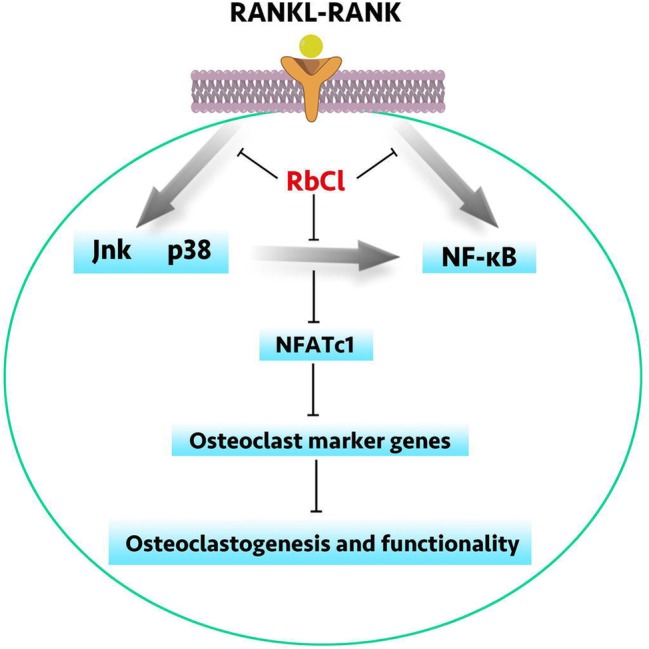
A schematic diagram of RbCl in regulating osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis. By targeting Jnk and p38-mediated NF-κB activation, RbCl attenuated RANKL-induced expressions of osteoclast marker genes to inhibit osteoclastogenesis and functionality in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, RbCl could also enhanced ALP activity and mineralization in vivo and in vitro, thereby re-establishing the homeostasis of bone microenvironment to provide the potent possibility for future translational practice in clinic, such as the surface coating of orthopedic implant.
