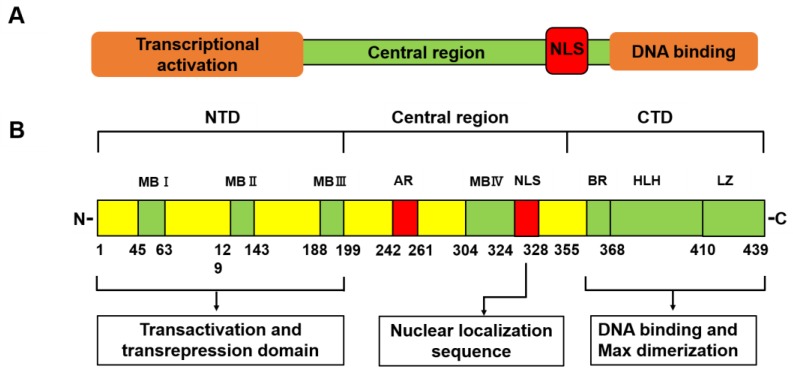
Figure 1.
Structures of Myc family proteins (A). Mammalian Myc proteins consist of a transcriptional activation domain, a central region, a nuclear localization sequence (NLS), and an area involved in DNA binding. Structures of human c-Myc protein (B). The N-terminal transactivation domain (NTD) includes three conserved regions named as Myc box-I, II, and III (MBI, MBII, and MBIII) and the acidic region (AR). MBI and MBII are necessary for Myc transcriptional and cell-transforming activity as well as recruitment of Myc transactivation. MBIII regulates transcriptional suppression. In the central region, MBIV is involved in apoptosis, transformation and modulation of DNA-binding. The C-terminal domain (CTD) includes the basic, the helix-loop-helix, and the leucine zipper domains (b-HLH-LZ) and is necessary for dimerization with Myc associated protein X (MAX).