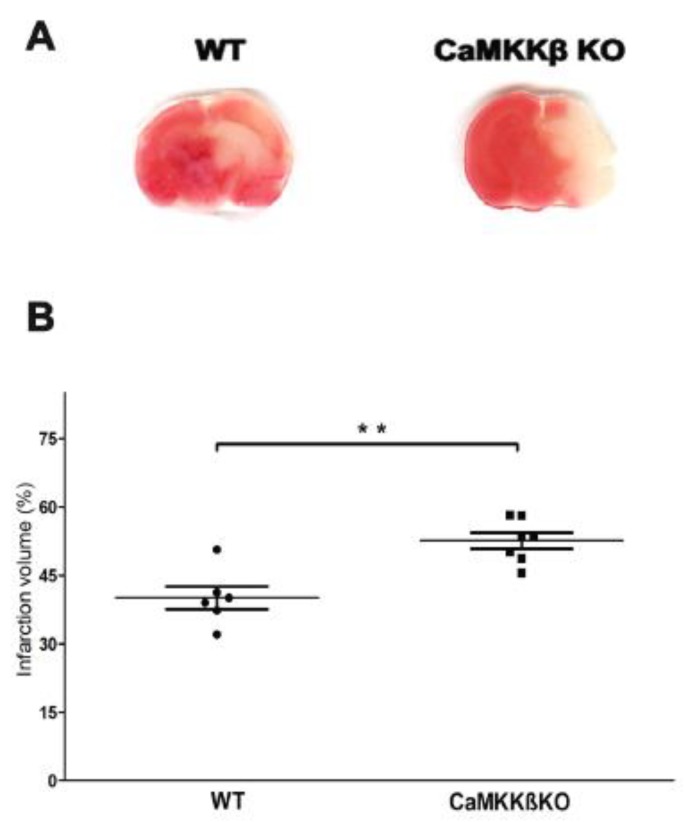
Figure 1.
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase (CaMKK) β knockout (KO) mice had larger infarcts than the wild-type (WT) mice, assessed 24 h after HI. (A) Representative TTC stained coronal brain sections from WT and CaMKK β KO HI mice are shown. (B) Quantification of infarct volume revealed that deletion of CaMKK β produced elevation in the infarct volume (n = 6–7 per group, ** p < 0.01 versus WT HI; vertical bars indicate SEM).