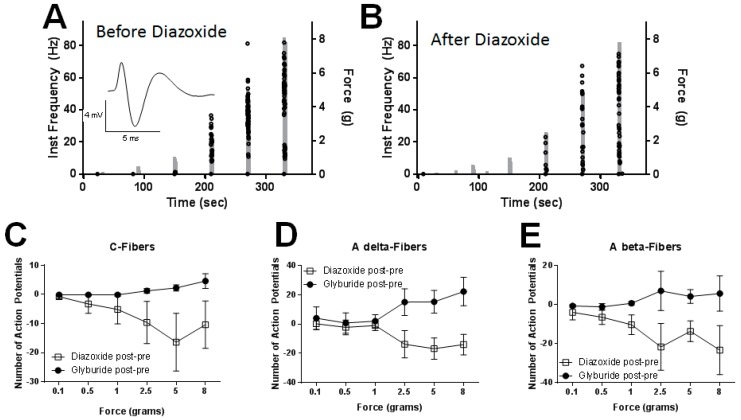
Figure 10.
The SUR1 agonist, diazoxide, decreases mechanical responsiveness of unmyelinated, C-fibers. (A) Increase in number (dots) and peak instantaneous frequency (left y-axis) of C-fiber action potentials as the force of stimulation is increased in a step-wise fashion (right y-axis). Inset: Example trace from recording. (B) Application of diazoxide (100 uM, 10 min) to the receptive field of a C-fiber decreases the number of action potentials compared to before application. (C) Diazoxide decreases C-fiber responses to increasing mechanical stimulation in SNL mice (F (5,70) = 3.70, p = 0.025); Tukey post-hoc comparing 0.1 g versus 5 g and 8 g; 95% CI = 3.05 to 28.2 and 0.55 to 25.7, respectively; n = 8/group). Glyburide application did not significantly change the number of action potentials across mechanical forces. No significant changes in number of action potentials post drug application were found in myelinated A delta-fibers (D) or A beta-fibers (E). Data presented as number of action potentials after drug application subtracted from the number of action potentials during the same time period before drug application.